OHV Gasoline Engines Ford Escort 4
General OHV engine data
The engine is a gasoline, four-stroke, four-cylinder, in-line, water-cooled, mounted transversely in front of the car. OHV engines (OHV – Overhead valves) with a...
The engine is a gasoline, four-stroke, four-cylinder, in-line, water-cooled, mounted transversely in front of the car. OHV engines (OHV – Overhead valves) with a...
Main parameters of OHV engines
Engine designation 1,1 HC OHV 1,1 HC OHV 1,3 HC OHV 1,3 HC 2V OHV Engine code GLB GSG JLA/ JLB JBB/ JBA Working volume, cm 3 1117 1117 1297 1297 Power, kW, HP, at rpm 40...
Engine designation 1,1 HC OHV 1,1 HC OHV 1,3 HC OHV 1,3 HC 2V OHV Engine code GLB GSG JLA/ JLB JBB/ JBA Working volume, cm 3 1117 1117 1297 1297 Power, kW, HP, at rpm 40...
Cylinder Head — Specifications
Cast iron cylinder head with in-line valves. Valve guides Valve guides made of special cast iron are pressed into the cylinder head. Inlet and outlet valve guide inner...
Cast iron cylinder head with in-line valves. Valve guides Valve guides made of special cast iron are pressed into the cylinder head. Inlet and outlet valve guide inner...
Engine Block — Specifications
The engine block is cast iron. The cylinders are made directly in the cylinder block. Cylinder diameters, mm: - nominal: 1 73,940 – 73,950 2 73,950 – 73,960 3 73,960 –...
The engine block is cast iron. The cylinders are made directly in the cylinder block. Cylinder diameters, mm: - nominal: 1 73,940 – 73,950 2 73,950 – 73,960 3 73,960 –...
Crank Mechanism — Specifications
Crankshaft The steel crankshaft is supported by three bearings. Axial play 0.09 - 0.30 mm Diameters of main journals: - nominal size 56.990 – 57.000 mm - nominal size...
Crankshaft The steel crankshaft is supported by three bearings. Axial play 0.09 - 0.30 mm Diameters of main journals: - nominal size 56.990 – 57.000 mm - nominal size...
Gas distribution system — specifications
The camshaft is located in the cylinder block, drives the valves via tappets and valve levers, and is driven by a chain. Valve clearance (cold): - inlet 0.22 mm –...
The camshaft is located in the cylinder block, drives the valves via tappets and valve levers, and is driven by a chain. Valve clearance (cold): - inlet 0.22 mm –...
Fuel System — Specifications
Fuel tank Manufactured from stamped sheet metal and mounted in front of the rear axle of the vehicle. Tank capacity: 40 l. Fuel pump The mechanical diaphragm pump is...
Fuel tank Manufactured from stamped sheet metal and mounted in front of the rear axle of the vehicle. Tank capacity: 40 l. Fuel pump The mechanical diaphragm pump is...
Ignition system — specifications
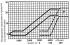
Characteristics of the ignition timing of the ignition distributor Bosch engine 1.1 dm 3 A - centrifugal regulator; B - vacuum regulator The Bosch contact ignition...
Characteristics of the ignition timing of the ignition distributor Bosch engine 1.1 dm 3 A - centrifugal regulator; B - vacuum regulator The Bosch contact ignition...
Lubrication system — specifications
Oil pump The gear oil pump with built-in relief valve is mounted on the side of the engine block and is driven by the camshaft. Oil pressure generated by the pump at...
Oil pump The gear oil pump with built-in relief valve is mounted on the side of the engine block and is driven by the camshaft. Oil pressure generated by the pump at...
Cooling System — Specifications
Coolant Coolant change: once every two years. The ratio of Ford concentrate and water for the preparation of coolant operating at temperatures down to minus 30°C 50/ 50...
Coolant Coolant change: once every two years. The ratio of Ford concentrate and water for the preparation of coolant operating at temperatures down to minus 30°C 50/ 50...
Tightening torques for threaded connections
Cylinder head bolts on vehicles manufactured before 09.1988: – 1st stage 12 – 15 Nm – 2nd stage 45 – 55 Nm – 3rd stage 85 – 90 Nm – 4th stage (15 minutes after stage 3)...
Cylinder head bolts on vehicles manufactured before 09.1988: – 1st stage 12 – 15 Nm – 2nd stage 45 – 55 Nm – 3rd stage 85 – 90 Nm – 4th stage (15 minutes after stage 3)...
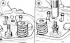
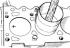
General view of the OHV engine and engine compartment
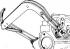
Engine compartment with engine 1.3 dm 3 (Valencia) with VV carburetor 1 - right stand; 2 - battery; 3 - oil level meter; 4 - heater air intake; 5 - carburetor; 6 -...
Engine compartment with engine 1.3 dm 3 (Valencia) with VV carburetor 1 - right stand; 2 - battery; 3 - oil level meter; 4 - heater air intake; 5 - carburetor; 6 -...
Valve clearance adjustment
OHV engine intake and exhaust valves, except for 1.3 dm 3 engine manufactured from September 1988 A - inlet; E - graduation The optimal clearance in the gas distribution...
OHV engine intake and exhaust valves, except for 1.3 dm 3 engine manufactured from September 1988 A - inlet; E - graduation The optimal clearance in the gas distribution...
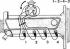
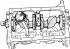
Removing the cylinder head
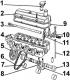
Cylinder head 1 - oil filler neck; 2 - head cover; 3 - the axis of the levers; 4 – a head of the block of cylinders; 5 - camshaft sprocket; 6 - chain; 7 - camshaft...
Cylinder head 1 - oil filler neck; 2 - head cover; 3 - the axis of the levers; 4 – a head of the block of cylinders; 5 - camshaft sprocket; 6 - chain; 7 - camshaft...
Dismantling of a head of the block of cylinders
1. Position the cylinder head at the front and rear on two pieces of wood. 2. Remove the intake and exhaust manifolds along with the carburetor. 3. Compress the valve...
1. Position the cylinder head at the front and rear on two pieces of wood. 2. Remove the intake and exhaust manifolds along with the carburetor. 3. Compress the valve...
Check and repair of a head of the block of cylinders
These procedures are performed after disassembling the cylinder head. Before checking, all parts must be cleaned and thoroughly blown out with compressed air. Attention!...
These procedures are performed after disassembling the cylinder head. Before checking, all parts must be cleaned and thoroughly blown out with compressed air. Attention!...
Cylinder head assembly
Installation of oil seals A - exhaust valve; B - inlet valve The slinger cap shown in the illustration must only be installed with an inlet valve that does not have the...
Installation of oil seals A - exhaust valve; B - inlet valve The slinger cap shown in the illustration must only be installed with an inlet valve that does not have the...
Installing the cylinder head
1. Thoroughly clean the holes for the cylinder head bolts from oil. 2. Install a new head gasket to the engine block. On vehicles built since 9/88, an asbestos-free...
1. Thoroughly clean the holes for the cylinder head bolts from oil. 2. Install a new head gasket to the engine block. On vehicles built since 9/88, an asbestos-free...
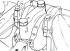
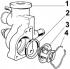
Replacement of a forward sealing ring of a cranked shaft
1. Remove ground wire from battery. 2. Loosen the lower mounting bolts and the upper alternator tension bolt, tilt the alternator towards the engine and remove the drive...
1. Remove ground wire from battery. 2. Loosen the lower mounting bolts and the upper alternator tension bolt, tilt the alternator towards the engine and remove the drive...
Pistons and connecting rods — removal
1. Remove cylinder head and oil sump. 2. Check the numbers on the connecting rod caps and connecting rods and their position. Connecting rod No. 1 is located on the...
1. Remove cylinder head and oil sump. 2. Check the numbers on the connecting rod caps and connecting rods and their position. Connecting rod No. 1 is located on the...
Pistons and connecting rods — check and repair
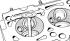
Mutual position of piston ring locks The service life of the engine without cylinder boring can be significantly increased by installing a special oil scraper piston...
Mutual position of piston ring locks The service life of the engine without cylinder boring can be significantly increased by installing a special oil scraper piston...
Pistons and connecting rods — installation
Attention! Always replace the 4-piston set with the pins. If it is necessary to grind one cylinder, grind everything and replace all pistons together with the fingers....
Attention! Always replace the 4-piston set with the pins. If it is necessary to grind one cylinder, grind everything and replace all pistons together with the fingers....
Removing the engine
The engine is removed from the car along with the gearbox from under the car. If the gearbox is previously removed, the engine is removed from the engine compartment...
The engine is removed from the car along with the gearbox from under the car. If the gearbox is previously removed, the engine is removed from the engine compartment...
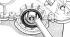
Engine disassembly
Thermostat 1 - thermostat housing; 2 - sealing ring; 3 - thermostat; 4 - latch Camshaft chain drive 1 - crankshaft oil flinger ring; 2 – an asterisk of a camshaft; 3 -...
Thermostat 1 - thermostat housing; 2 - sealing ring; 3 - thermostat; 4 - latch Camshaft chain drive 1 - crankshaft oil flinger ring; 2 – an asterisk of a camshaft; 3 -...
Engine repair
1. Check the ovality, taper and size of the main and connecting rod journals of the crankshaft. 2. When the connecting rod journals of the crankshaft are reduced by 0.25...
1. Check the ovality, taper and size of the main and connecting rod journals of the crankshaft. 2. When the connecting rod journals of the crankshaft are reduced by 0.25...
Engine assembly
1. Lubricate the camshaft support bearings and insert it into the cylinder block. 2. Install the camshaft mounting plate and check its axial play. 3. Install pushers to...
1. Lubricate the camshaft support bearings and insert it into the cylinder block. 2. Install the camshaft mounting plate and check its axial play. 3. Install pushers to...
Engine installation
1. Place the engine with gearbox under the engine compartment of the vehicle, hook it with a lifting mechanism and, being careful, raise it to a position where you can...
1. Place the engine with gearbox under the engine compartment of the vehicle, hook it with a lifting mechanism and, being careful, raise it to a position where you can...
Cylinder compression check
The compression value shows, in most cases, how worn out the cylinder-piston group of the engine. To measure compression, a compression gauge with a maximum reading of...
The compression value shows, in most cases, how worn out the cylinder-piston group of the engine. To measure compression, a compression gauge with a maximum reading of...
This section is available on russian, bulgarian, belarusian, ukrainian, serbian, croatian, romanian, polish, slovak, hungarian
Escort 5
Escort 4
Escort 3
- General information
- User manual
- Maintenance
- Engine
- HCS and Endura-E engines
- CVH and PTE engines
- Zetec and Zetec-E engines
- Gasoline engines
- Diesel engines
- Diesel engines (since 1992)
- Cooling and heating
- Carburetors
- CFI fuel injection
- EFI fuel injection
- SEFI fuel injection
- Exhaust system
- Charging and starting system
- Ignition system
- Transmission
- Clutch
- Mechanical gearbox
- Automatic gearbox
- Drive shafts
- Chassis
- Brake system
- Car suspension
- Steering
- Body
- Electrical equipment
- Light and appliances
- Schematic diagrams
Escort 4
- General information
- User manual
- Maintenance
- Gasoline engines
- OHV engine repair
- CVH engine repair
- Fuel system
- Weber 2V carburetor
- KE-Jetronic injection system
- CFI injection system
- Ignition system
- Diesel engines
- Engine repair
- Fuel system
- High pressure pump
- Cooling and lubrication system
- Transmission
- Clutch
- Mechanical gearbox
- Automatic gearbox
- Drive shafts
- Chassis
- Suspension and wheels
- Steering
- Brake system
- Body
- Body elements
- Doors, locks and windows
- Electrical equipment
- Equipment and devices
- Lighting system
- Electrical circuits
Escort 3
- General information
- Maintenance
- Characteristics
- Engine
- Disassembly and assembly
- Cooling system
- Lubrication system
- Supply system
- Fuel injection «K-Jetronic»
- Transmission
- Clutch
- Mechanical gearbox
- Hydromechanical box
- Drive shafts
- Chassis
- Front suspension
- Rear suspension
- Steering
- Brake system
- Electrical equipment
- Starting and charging system
- Ignition system
- Ignition «Escort RS 1600»
- Light and appliances
- Schematic diagrams
FordBook.ru © 2014-2024 • Mobile version • Interesting to read • Sitemap: EN BG BY UA RS HR RO PL SK HU • Site search • Contact with administration
Focus 1 • Focus Turnier 1 • Focus 2 • Mondeo 1 • Mondeo 1 and 2 • Mondeo 2 • Mondeo 3 • Mondeo 4 • Escort 3 • Escort 4 • Escort 5 • Fiesta 2 • Fiesta 4 • Taurus 1 and 2 • Fusion • Scorpio 1 • Scorpio 2 • Sierra •
Focus 1 • Focus Turnier 1 • Focus 2 • Mondeo 1 • Mondeo 1 and 2 • Mondeo 2 • Mondeo 3 • Mondeo 4 • Escort 3 • Escort 4 • Escort 5 • Fiesta 2 • Fiesta 4 • Taurus 1 and 2 • Fusion • Scorpio 1 • Scorpio 2 • Sierra •