Exhaust System
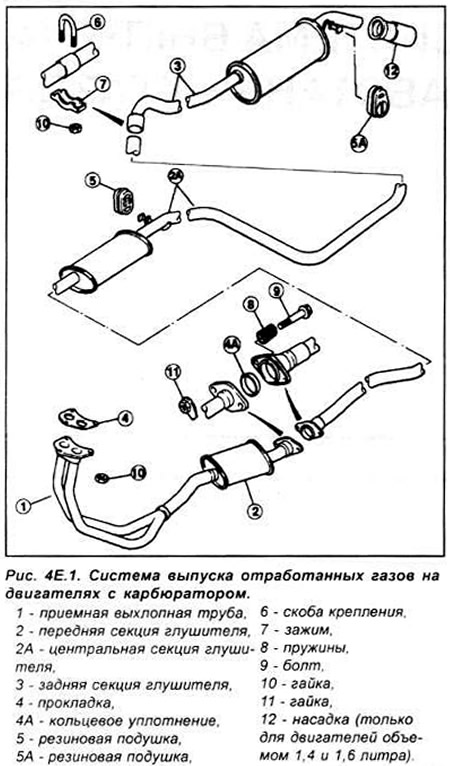
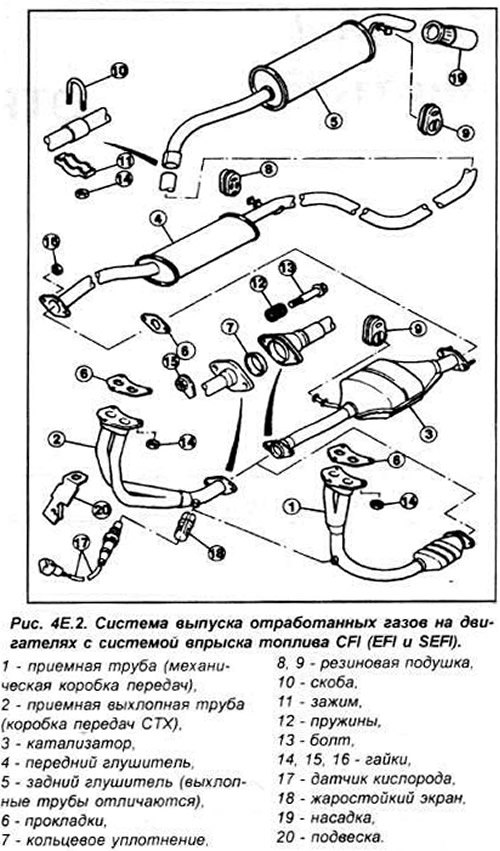
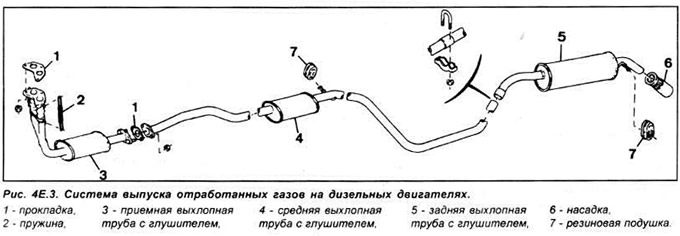
The exhaust system includes an exhaust manifold, front exhaust pipe, catalytic converter and 2 mufflers. The exhaust system consists of three sections: front pipe with catalytic converter intermediate pipe and front muffler rear muffler and exhaust pipe. The system is suspended along its entire length on rubber cushions.
Emission control system
To minimize air pollution from incompletely burned and evaporated gases, as well as to save fuel, several different systems are used:
- engine management system (fuel and ignition control system);
- crankcase ventilation system (PCV);
- fuel evaporation control system (EVAP);
- waste gas re-burning system (EGR);
- pulsating air system (PAIR);
- catalyst.
Crankcase ventilation system
Some of the combustion products break through the piston rings into the crankcase and, if not taken appropriately, they can enter the atmosphere. To prevent this, the crankcase is connected by a ventilation hose to the air filter so that the crankcase gases are mixed with the air-fuel mixture and re-burned in the engine cylinders.
On HCS engines, the system consists of a filter in the oil filler plug and a hose connecting the filler neck to the back of the air filter housing. An additional hose connects the air filter to the intake manifold. At idle speed and at low engine loads, crankcase gases are sent to the exhaust manifold without afterburning. Additional air is supplied through 2 small holes located next to the valve in the air filter housing, the purpose of which is to prevent the creation of a large vacuum. With an increase in engine load, when the vacuum in the intake manifold decreases, the valve opens, and crankcase gases are directed through the air filter housing, where they are mixed with the fuel mixture and afterburned. The principle of operation of the crankcase ventilation system on Endura-E engines is similar to that described.
CVH and PTE engines use a closed crankcase ventilation system. It is the same as previously described except that the crankcase ventilation hose connects directly to the head cover.
On Zetec and Zetec-E engines, the oil separator is mounted on the front side of the cylinder block, and a set of valves in a rubber sealing ring is located at the upper end of the separator.
Fuel Evaporation Control System
This system is designed to prevent fuel vapor from entering the atmosphere. The fuel tank has an expansion tank and vent pipes that are designed so that no fuel or steam can escape even if the car gets very hot. The ventilation tubes are connected to a canister containing charcoal that absorbs hydrocarbon vapors. When the engine is stopped, fuel vapor is collected in a charcoal canister. When the engine is started, fresh air is sucked in through the canister and vapors are drawn from the canister to the air filter and into the engine where they are burned.
Exhaust Gas Re-burning System
This system is installed on Zetec-E engines. reduces the content of nitrogen oxide in exhaust gases. This is achieved by re-circulating some of the exhaust gases through the EGR valve to the intake manifold.
The system consists of EGR valve, EGR exhaust gas differential pressure sensor, EGR solenoid valve, ECU system and various sensors. The ECU is programmed to produce the ideal EGR valve lift for all operating conditions.
Air pulsation system
The system consists of a one-way air pulsation solenoid valve, hoses and a control valve. The system introduces filtered air directly into the exhaust ports, using the change in exhaust gas pressure to push additional air from the filter into the exhaust system when the exhaust pressure is below atmospheric pressure. The valve only allows gases to pass in one direction and there is no risk of exhaust gases blowing through to the air filter.
The main function of the system is to increase the temperature of the exhaust gases at start-up, which reduces the time for the catalyst to warm up.
Catalyst
The catalyst stimulates a chemical reaction to convert the carbon monoxide and hydrocarbons in the exhaust gases into carbon dioxide and water. The catalyst does not require any maintenance, but should be checked periodically for signs of physical damage. The catalyst contains a ceramic insert which is very fragile and may break if the catalyst is struck or dropped.
Visitor comments