Withdrawal
Loosen toothed belt tension (see the corresponding description in the section "Removing the toothed belt").
Remove the toothed belt. Do not rotate the crankshaft with the toothed belt removed. Unscrew the bolts securing the camshaft pulleys and remove the pulleys (see fig. 2С.25).

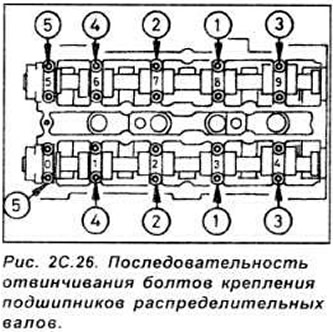
Working in sequence, loosen the camshaft bearing cap bolts half a turn each pass until the bots are completely unscrewed. This is necessary to gradually and evenly relieve the pressure of the valve springs (see fig. 2C.26).
Remove the covers, checking their markings and the presence of guide pins, then remove the camshafts and oil o-rings. The intake camshaft can be identified by the camshaft position sensor ridge (see fig. 2C.27, 2C.28).


Using a rubber suction cup, remove each hydraulic tappet and turn it over to prevent oil from leaking from the tappet. Place the tappets in an appropriate container which must be filled with clean engine oil. Position the hydraulic tappets so that they can be installed in their places (see fig. 2C.29, 2C.30).


Examination
Check the condition of the camshafts and hydraulic tappets.
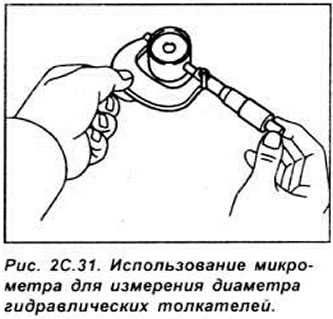
Measure the outer diameter of the pushers with a micrometer, as well as the taper of the cylindrical part of the pusher.
If valve knocking is heard when starting a cold engine, and the hydraulic tappets are in good condition, it is necessary to change the engine oil and filter and use only engine oil of good quality and the required viscosity.
Check the camshaft lobes for scratches, pitting and wear. If there are defects, the camshaft must be replaced.
Check the condition of the camshaft bearings and cylinder head bearings for wear.
Measure the diameter of each camshaft journal at several points with a micrometer. If the diameter of any neck is less than required, the camshaft must be replaced.
To check the operating clearance of the camshaft bearings, remove the hydraulic tappets and, using an appropriate solvent, carefully clean the bearing surfaces, then install the camshafts and place a piece of Plastigage gauge along each camshaft bearing journal. install the bearing caps and tighten them to the required torque. Remove the bearing caps and use a scale ruler to measure the width of the measuring rod. Depending on the width of the crushed measuring rod, use the scale bar to determine the size of the gap. Using a soft tool, remove the measuring rod from the camshaft journals.
If the operating clearance of any bearing exceeds the allowable limits, replace the camshaft with a new one and repeat the measurements. If the gap again exceeds the allowable value, the head must be replaced.
To check camshaft play, remove hydraulic tappets, clean bearing surfaces, and install camshafts and bearing caps. Measure the backlash using a dial indicator, the measuring tip of which should rest against the right end of the camshaft.
Move the camshaft to the indicator, set the indicator to zero. and move the camshaft as far away from the indicator as possible. The value of the measured backlash will be displayed on the indicator scale. If the backlash value exceeds the allowable value, repeat the measurement. If the backlash again exceeds the allowable value, the head must be replaced.
Installation
Lubricate the hydraulic tappet seats in the cylinder head and the hydraulic tappets. Insert the hydraulic tappets into the sockets in which they were before removal.
Attention. If new hydraulic tappets are used, they must be filled with engine oil before installation.

Lubricate the camshaft bearings and cams with engine oil and install the shafts in place, positioning the shafts so that the grooves in the left end of the shafts are parallel and above the mating surface of the cylinder head.
Check that the guide pins are in place and that the mating surface is completely clean. Apply a light coat of Loctite 518 to the mating surfaces of the right camshaft bearing caps. Install new camshaft oil seals (see fig. 2C.34).


All camshaft bearing caps are marked with a single number indicating the cap number. Intake camshaft bearing caps are numbered 1 to 4 and exhaust camshaft bearing caps 5 to 9. Each cap must be installed with the numbered side surfaces facing outward of the engine (see fig. 2C.34).
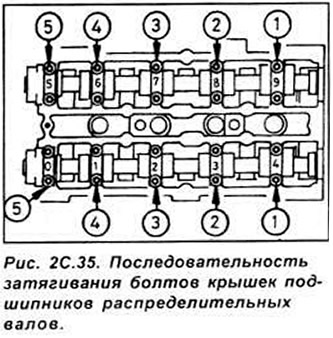
Tighten the bearing cap bolts gradually and in sequence, turning each bolt half a turn in one pass, until each cap contacts the cylinder head. Then, in the same sequence, tighten the bolts in two stages to the required torque. Gradual and even tightening of the bolts is necessary to evenly compress the valve springs (see fig. 2C.35, 2C.36).

Wipe off any excess sealant so that it does not enter the oil passages. The engine can be started no earlier than one hour after applying the sealant.
Install new camshaft oil seals
Install the camshaft pulleys on the shafts, hand-tightening the pulley bolts. Install the toothed belt on the pulleys, and finally tighten the bolts, while using a special tool to keep the pulleys from turning. Further installation is carried out in the reverse order of removal.
Visitor comments