The suspension of a comfortable and reliable Fiesta car is made at a high technical level. The front independent suspension includes McPherson struts and L-shaped wishbones. The rear combined beam with transverse levers rests on the shock absorber struts.
Even with the use of computer technology, the development and design of a car's suspension is a serious and complex task: the wheels must be located at precisely defined angles with respect to the car's axle. However, when the wheel hits a bump on the road surface or when cornering at high speed, the geometry of the wheels is forced to change. Of course, the wheels should not lose contact with the road surface. The contact of the wheels with the road surface is provided by the suspension. The suspension absorbs the impact of bumps in the road surface. Shock absorbers dampen unwanted subsequent vibration, they weaken not shocks, but their own vibration of the suspension.
Steering and safety
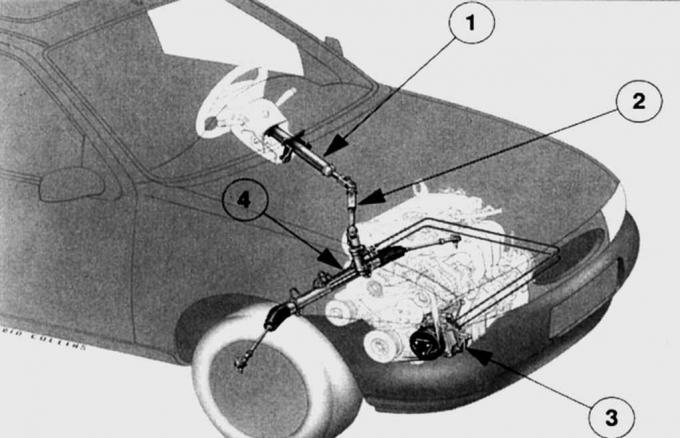
Pic. 13.1. An arrangement on the car of elements of a steering with the amplifier: 1 – the top part of a steering column; 2 – the bottom part of a steering column; 3 – the pump of the amplifier of a steering; 4 - steering mechanism
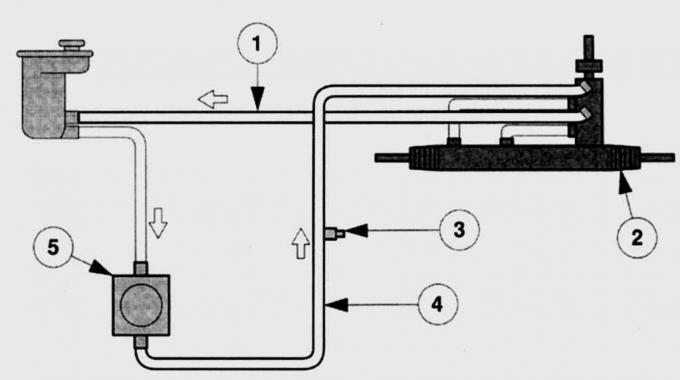
Pic. 13.2. The scheme of functioning of the power steering (PAS): 1 - return pipeline; 2 - steering gear with gear rack; 3 – the switch of pressure of system of the amplifier of a steering; 4 - pressure pipeline; 5 – the pump of the amplifier of a steering
Steering (pic. 13.1, 13.2) refers to the elements of active safety. It should be light and immediately respond to the steering wheel. The rack and pinion steering is mounted on the axle beam behind the engine. The two-piece steering shaft directly acts on the rack, to the ends of which the left and right steering rods are respectively attached. When the steering wheel is turned, forces are transmitted through the tie rod ends to the steering knuckle and wheels.
The chassis of the Ford Fiesta is a good example of the fact that the creators of modern compact cars do not save on comfort and driving safety. McPherson shock absorbers work in the front of the car, and the rear suspension beam relies on similar shock absorbers. They are guided by a combined transverse beam with rigidly fixed trailing arms that determine the wheel track.
Visitor comments