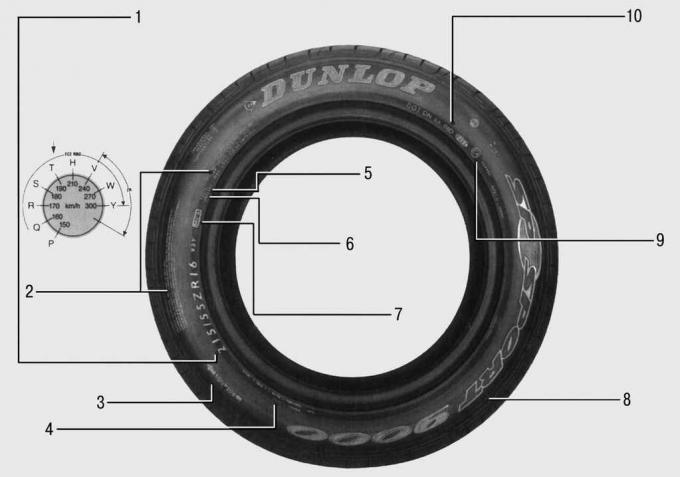
Pic. 13.30. Designations on the sidewall of the tire: 1 - tire marking: 215 - tire width in mm; 55 - the ratio of the height of the tire profile to its width in percent; ZR - radial tire; 16 - landing diameter in inches; 93 - load (650 kg); Y - maximum speed (300 km/h); 2 - data for North America: permissible highest load and maximum permissible air pressure, as well as an indication of safety measures; 3 – direction of tire rotation; 4 - design: data on the quantity and material of the tread and sidewall of the tire are given; 5 - radial tire: in a radial tire, the cord is located at an angle of 90°to the direction of rotation of the tire; 6 - tubeless tire: the inner airtight layer replaces the tube; 7 - MFS wheel rim protection; 8 - TWI tread wear indicators: marking «TWI» or triangles on the tire sidewall indicate the location of the tread wear indicators. When the minimum profile depth is reached (1.6 mm) transverse plates are exposed; 9 - signs of verification: number E - the tire complies with European requirements ECE-R30; digit 4 - code of the country in which the tire was tested (Netherlands); 10 - DOT symbols: the tire meets the requirements of the US Department of Transportation (Department of Transportation) DM 6P 38 T - DOT code (tire manufacturer, size and design coding): 219 - date of manufacture (the first and second digits are the week of manufacture, the third digits are the year of manufacture); in the example: 21st week of 1999 (since 2000, a four-digit designation has been used, for example, 1500-15th week of 2000)
The characteristics of modern tires - size, external load, internal pressure and maximum recommended driving speed - are standardized to ensure interchangeability of tires during their operation (pic. 13.30). According to current worldwide agreements, tire sizes are given in millimeters or both in millimeters and inches. For example, marking 155/70 R 13 means that the width of the tire in an unloaded state is 155 mm. The next two digits indicate the ratio of the height to the width of the cross section of the tire profile - 70%. The smaller this ratio, the flatter and wider the tire is. Letter «R» characterizes the design of the tire - radial (a tire with a radial arrangement of cord threads). The following numbers define the inside diameter of the tire in inches. When purchasing a new tire, pay attention to its characteristics: the new tire must fit the rim.
Only radial tires are installed on passenger cars.
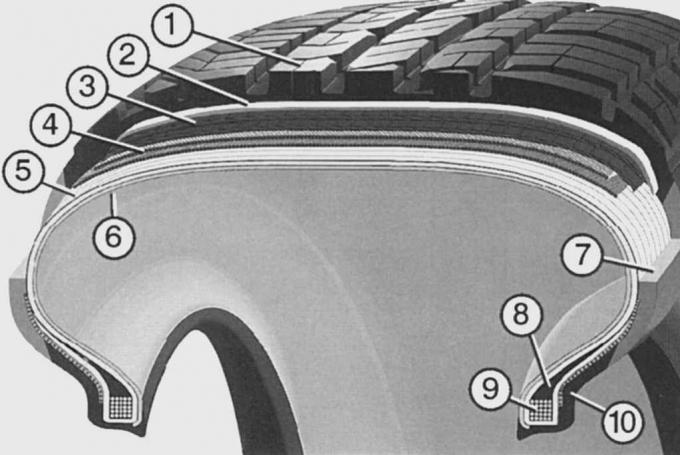
Pic. 13.31. Tubeless tire of radial design PKW-Reifens: 1 - tread (profile and location affect the quality of the tire); 2 - base (reduces rolling resistance); 3 - nylon cord (increases resistance to high speeds); 4 - steel breaker (improves driving stability); 5 - tire carcass (provides shape and strength to the tire); 6 - airtight inner layer replacing the chamber; 7 - sidewall (protects the frame from damage); 8 - board (maintains precise control and movement); 9 - bead core (provides a firm fit on the rim); 10 - reinforcing thickening (improves control accuracy and driving stability)
In radial tires, the cords are located along the shortest path between the tire beads. The breaker belt surrounds the thin and resilient carcass and provides stability to the tire (pic. 13.31).
Tubeless tires feature a vulcanized inner layer with high airtightness. The bead of such a tire must be installed securely and tightly on the wheel rim. The absence of a tube in the tire reduces the mass of the wheel and simplifies its installation on the wheel rim.
Speed index - capital letter after the last digit
The uppercase letter after the last number on the sidewall indicates the maximum tire speed allowed.
Tire 155/ 70 R 13 with letter «S» it is permissible to use up to a maximum vehicle speed of 180 km/h, with the letter «T» – up to 190 km/h. For a maximum speed of 210 km/h, tires marked «H». regular tires (M+S) with the designation «Q» designed for speeds up to 160 km/h.
The DOT symbol indicates the age of the tire
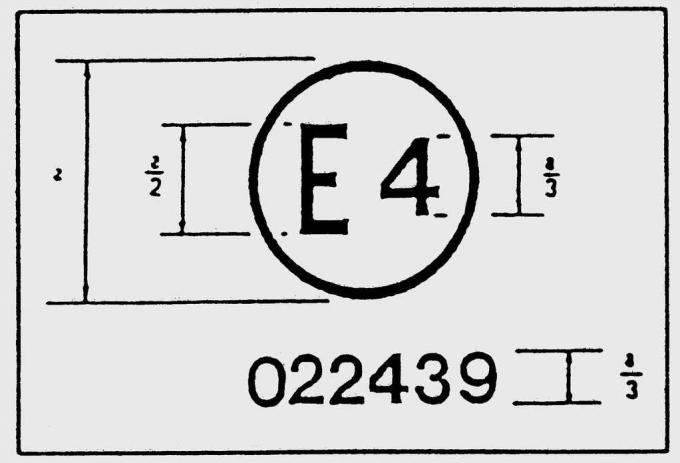
Pic. 13.32. The ECE test number is determined by a capital letter «E» and the number of the country of origin, for example, «1» for Germany, «4» for the Netherlands
The actual production date of the tire is determined by the DOT number on the sidewall of the tire: since 1990, these numbers have been followed by a small triangle. The DOT 1500 number means that the tire was produced in the 15th week of 2000. New tires manufactured from October 1, 1998 must carry the ECE test number on the sidewall (pic. 13.32). Each test number guarantees that the tire has passed the Economic Commission for Europe quality standard (ECE-R30). If your vehicle is fitted with tires with a DOT number greater than 408 and no ECE test number, then you are operating a tire without «general operating permit».
Winter tires
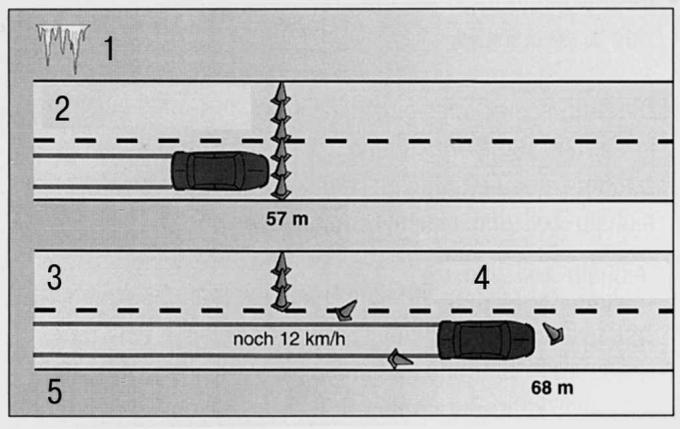
Pic. 13.33. Comparison of the braking distances of summer and winter tires of a car without ABS: 1 - braking on ice with wheel lock (speed 30 km/h); 2 - winter tires; 3 - braking distance; 4 - summer tires; 5 - braking distance
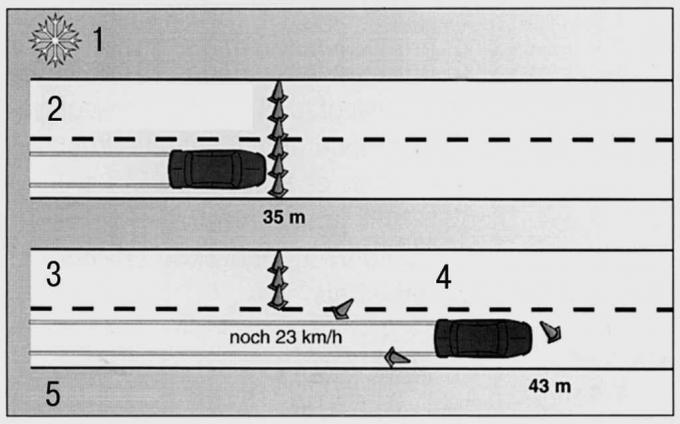
Pic. 13.34. Comparison of braking distances of summer and winter tires of a car with ABS: 1 - braking with ABS on a snowy road (speed 50 km/h); 2 - winter tires; 3 - braking distance; 4 - summer tires; 5 - braking distance
Even for operation on autumn roads, it is necessary to install winter tires on the car, and in winter you can’t do without them at all. This is due to the fact that the running surfaces of the tires are made of a special material based on rubber with a high content of natural rubber. The grip of these tires on wet, slippery roads and at temperatures below 7°C is much better than conventional summer tires (pic. 13.33, 13.34). The minimum profile depth of winter tires is 4 mm. In any case, on all four wheels, replace summer tires with winter tires - the combination of summer and winter tires is dangerous.
Winter tires are better to install on your wheels
Summer tires are prone to slipping on snow and ice, therefore, when driving a car in the winter season, it is recommended to install a set of tires with a winter tread pattern. Regardless of which tires are fitted to the vehicle, at temperatures near the freezing point, a thin film of water forms on the ice, which reduces the grip of tires, including winter tires.
Good winter tires don't have to be wide. Even though narrow tires are cheaper than wide tires, the money saved will have to be spent on a second set of suitable rims, because the constant removal and installation of summer and winter tires deteriorates their quality - it is better to purchase a second set of rims. By the way, after each tire change, the wheels must be re-balanced. The pressure in winter tires must be maintained at 0.2 bar more than in summer ones. If the permitted maximum speed of your winter tires is lower than the permitted maximum speed of the vehicle, affix a warning label to the instrument panel.
Checking the pressure in cold tires
It is necessary to measure the air pressure only in cold tires - during the movement they warm up, and the pressure in them increases. As a result, you get inaccurate measurement results. Check tire pressure every three to four weeks, a normal pressure drop per month should be 1.5%. If the pressure drop is greater, check the condition of the tire. With increased air pressure in hot tires, do not bleed air from the tire. With a significant change in load, the air pressure in the tires should be adjusted accordingly.
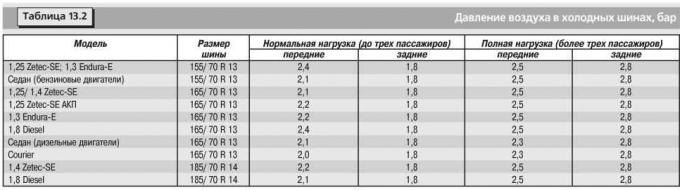
Regulatory values of air pressure in cold tires are given in Table. 13.2.
Tire valve caps
Tire valves must always be closed with protective caps, as once dirt gets into the valve, it will break the tightness of the tire, and the pressure in the tire will constantly decrease.
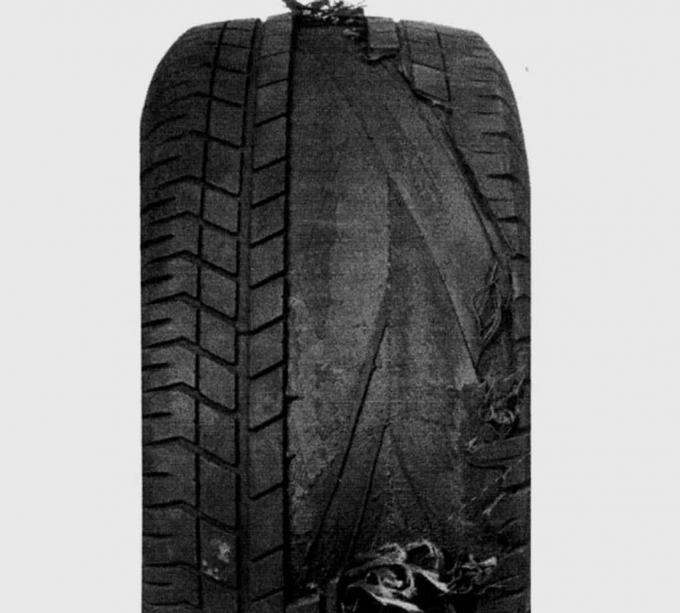

Pic. 13.35. Tire delamination due to overheating due to too low tire pressure
In no case should tires be operated with low pressure, as in this case their temperature exceeds the permissible limit, which will sooner or later lead to delamination of the tread or the tire will burst (pic. 13.35). Higher air pressure (by 0.2–0.3 bar) can even be beneficial: the steering becomes more sensitive and the fuel consumption is slightly reduced, but the car is still moving «tougher».
PRACTICAL ADVICE
Tire care
1. Never exceed the speed limit for your tires. First of all, this applies to tires (M+S) categories «Q» (160 km/h). At higher speeds, the tires wear out more, in the worst case, the tire may burst.
2. Avoid maximum driving speed when the vehicle is fully loaded. Check the temperature of the tire: if it is equal to body temperature, then everything is normal. Hot rubber is an alarm that indicates too low tire pressure or damage to the tire carcass. Remove such tires immediately and have them checked by a specialist.
3. If you often drive at high speeds on the motorway, install tires with a speed index that is an order of magnitude higher than indicated in the data sheet, for example, «T» instead of «S».
4. When parking, try not to run the sidewalls of the tires on curbs and other obstacles - they must be moved at low speed and at a right angle.
5. Increase tire pressure by 0.3 bar - this measure will save fuel without damaging the tires.
Visitor comments