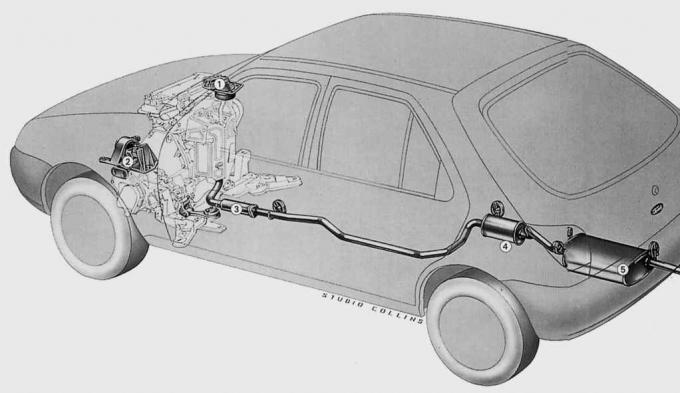
Pic. 11.0. Suspension on five rubber bearings of the Fiesta exhaust system, consisting of two parts: 1 - oxygen concentration sensor installed in the exhaust pipe; 2 - catalytic converter; 3 - flexible intermediate connector; 4 – central muffler; 5 - main muffler
The exhaust gas system ensures the removal of exhaust gases into the atmosphere, reducing the concentration of pollutants, reducing engine noise to the required level with minimal engine power loss. In order for the exhaust system to perform its functions, it must be in good condition.
Initially, exhaust systems were designed only to reduce noise from the combustion of fuel in the engine cylinders and directed exhaust gases into the atmosphere. In the 1980s, the exhaust system changed fundamentally: since then, catalytic converters have removed up to 90% of the harmful substances in the exhaust gases. The Fiesta is equipped as standard with a two-piece exhaust system. At the front of the vehicle, it consists of a controlled three-way catalytic converter (diesel engine with oxidation catalytic converter) and a flexible intermediate connector. The exhaust gases then pass into the atmosphere through the central and main mufflers. Heat shields in the area of the catalytic converter and muffler reduce the thermal effect on the underbody.
Service life of the exhaust system
When the air-fuel mixture is burned, among other things, water is formed, which contributes to corrosion from the inside of the exhaust system. The corrosion of the exhaust system increases as the temperature of the exhaust gases decreases. If you drive your car primarily in the city or for short distances, more condensate, soot and aggressive acids are deposited inside the exhaust pipes than when driving long distances with a fully warm exhaust system. However, as a rule, the elements of the Fiesta car's exhaust system work normally for about 70,000 km of the car's run.
• The front exhaust pipe with a catalytic converter and a flexible intermediate connector, through which exhaust gases exit at a temperature of 800-1000°C, is least affected.
• After the reaction in the catalytic converter, the exhaust gases gradually cool down and at the end of the exhaust pipe their temperature can drop to 200–350°C. This circumstance causes the appearance of a large amount of moisture condensate in the additional muffler, which mixes with the remnants of the combustion products and turns into aggressive acids, as a result, the metal of the exhaust system rusts from the inside.
• The front end of the exhaust system during long-distance travel experiences extreme conditions due to temperature differences, where hot metal is constantly splashed with water during rainy weather. Despite the flexible intermediate connector, thermal stresses can lead to pipe fracture or cracking.
• Regardless of the mode of operation, water splashes and saline solutions contribute to corrosion on the outside of the exhaust system. Stone impacts or hard road obstacles will shorten the life of the exhaust system, as will vibration due to damaged or missing exhaust system mounting parts. Harmful effects of temperature and vibration can cause the rubber suspension mounts to become brittle or break.
Visitor comments