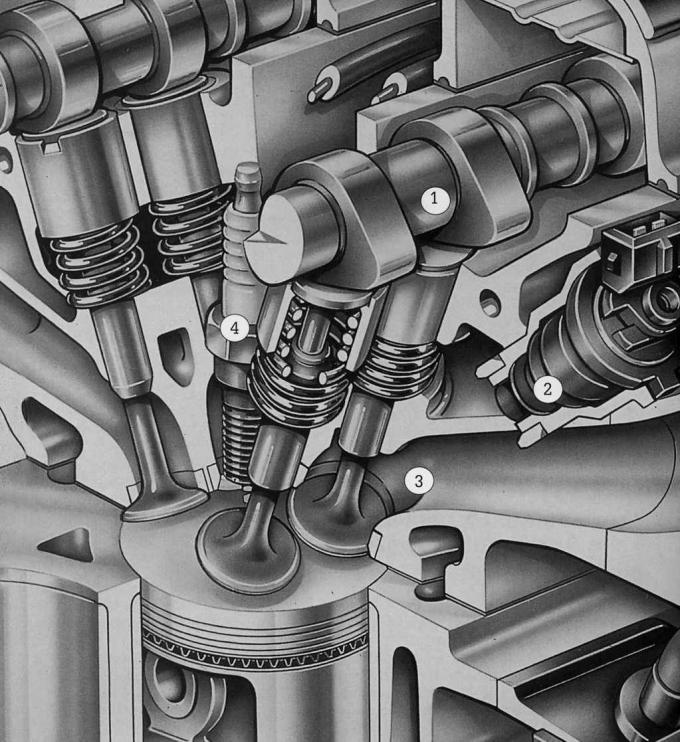
Pic. 8.0. The intake tract of the Zetec-SE engine: 1 - intake camshaft; 2 - nozzle; 3 - inlet channel; 4 - spark plug
Gasoline engines with fuel injection are quite powerful and at the same time economical engines. With the same fuel quality, fuel injection allows a slight increase in compression, in addition, electronic fuel metering is more accurate than in an engine with a carburetor. All this reduces fuel consumption, increases engine power and reduces exhaust emissions. Fiesta vehicles are no exception: since 1996, Ford has been equipping its engines with exclusively electronically controlled injection systems with programmed injection characteristics, ignition control and ignition timing, which ensure the preparation of a homogeneous air-fuel mixture in the intake tract by spraying fuel from four injectors. Systems such as fuel injection and ignition are no longer independent and become components of integrated engine management systems.
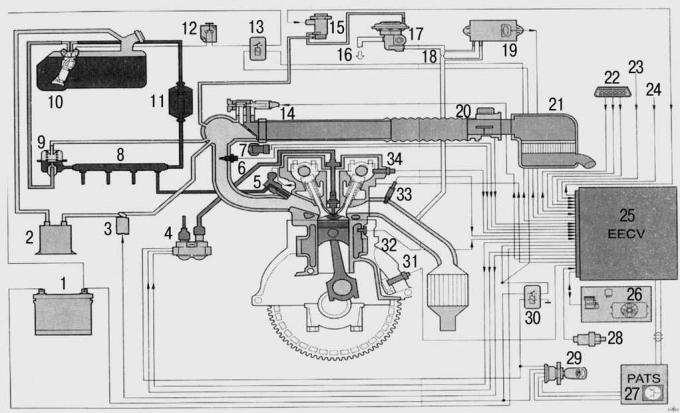
Pic. 8.1. Scheme of the fuel injection system of the Zetec-SE engine: 1 - battery; 2 - a tank with activated carbon; 3 - solenoid valve of the EAVAP fuel vapor recovery system; 4 - electronic ignition coil (El); 5 - nozzle; 6 - temperature sensor of the air entering the engine (IAT); 7 - throttle position sensor (TP); 8 - fuel distribution pipeline; 9 - fuel pressure regulator; 10 - fuel pump; 11 - fuel filter; 12 - battery safety switch (IFS); 13 - fuel pump relay (FPR); 14 – the valve of regulation of frequency of rotation of a cranked shaft of the engine idling (IAC); 15 - vacuum regulator of the exhaust gas recirculation system EGR (EVR); 16 - to the intake manifold; 17 - EGR exhaust gas recirculation valve; 18 - place for measuring the pressure drop; 19 – electronic differential pressure transducer (DPFE sensor); 20 - air flow meter (MAP); 21 - air filter housing and sound-absorbing pipe; 22 - diagnostic connector (DLC); 23 - from the service connector of the octane corrector (OAI); 24 – coupling of the compressor of the conditioner; 25 - VEEC control unit; 26 - switch of the fan of the air conditioning system; 27 - engine start blocking block (PATS); 28 - power steering switch (PSP); 29 - ignition switch with anti-theft device; 30 - power relay; 31 - crankshaft angle sensor (CKP); 32 - coolant temperature sensor (ECT); 33 - oxygen sensor (HO2S); 34 - camshaft position sensor (CMP)
Control units for fuel injection systems are absolutely maintenance-free; possible malfunctions and malfunctions can only be eliminated with comprehensive specialist knowledge and equipment. Therefore, the repair and maintenance of the Fiesta injection system must only be carried out at a service station. However, you need to know the basic criteria for preparing the air-fuel mixture in order to more accurately determine a possible malfunction and save money on expensive diagnostics. The following is a Ford injection system fitted to Zetec-SE engines (pic. 8.1).
Visitor comments