Master brake cylinder (GTZ): converts the path of the brake pedal into hydraulic force. When the brake pedal is released, the pressure in the system immediately disappears.
brake booster (servo brake): located in the engine compartment in front of the main brake cylinder. With each braking increases the mechanical force of the pedal by approximately 60%. Vehicles with ESP have an active brake booster. As soon as the electronic stability program is triggered in the Focus, the solenoid valve in the brake booster is activated. As a result, a pressure of approx. 10 bar is generated on the back of the diaphragm without actuating the brake pedal. The brake boosters draw their power through a hose directly from the intake manifold or a separate vacuum pump (diesel engine). During the braking process, the diaphragm connected to the GTZ piston rod reacts to the difference in pressure between atmospheric pressure and reduced pressure in the intake manifold.
Wheel brake cylinder (KTC): brake fluid pressure in the CTC can reach 120 bar. CTC pistons transmit pressure through a piping system to free-stroke pistons in brake collets (disc brake) or wheel brake cylinders (drum brake). The stroke of the piston is transmitted in disc brakes to the brake linings or the brake shoes in drum brakes.
Front axle
Brake disk: rotates synchronously with the axle hub. It removes the heat of friction to the atmosphere.
brake caliper seat: the brake caliper seat wraps around the Focus brake disc like a fist. On its inner side is a brake piston.
The brake pedal is pressed: system pressure created by the GTZ acts on the piston in the brake caliper seat and presses the inner brake lining against the brake disc. Due to this, the collet of the brake caliper, mounted on the slide bearings, moves inward and presses the outer brake lining against the brake disc in the same way.
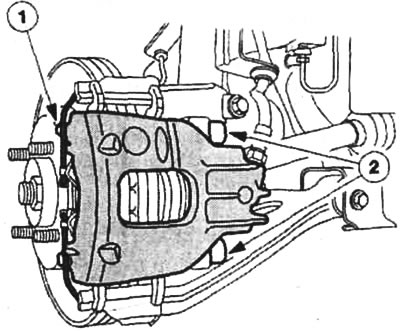
Disc brake with cam caliper: 1 - cam caliper; 2 - sliding pins.
The brake pedal is released: hydraulic pressure suddenly disappears, the piston gasket pulls the piston together with the brake caliper seat away from the brake discs. There is a slight gap between the brake linings and the disc - the brake disc rotates freely again.
Rear axle
Brake disk: rotates synchronously with the axle hub. It removes the heat of friction to the atmosphere.
brake caliper seat: the brake caliper seat wraps around the Focus brake disc like a fist. On its inner side is a brake piston.
Visitor comments