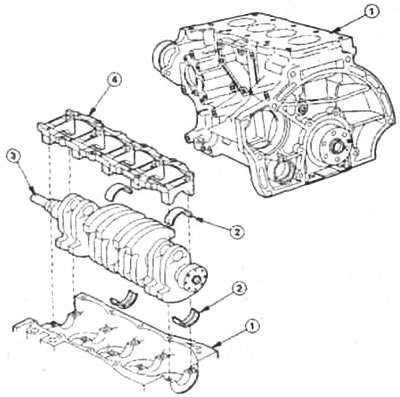
The Zetec-SE engine block is made of an aluminum-silicon alloy. Robustly built sidewalls and main bearing webs make the block particularly torsionally rigid. 1 - engine block; 2 - bearing shells; 3 - crankshaft with eight counterweights and five main bearings, 4 - main bearing jumper.
Cylinder head: in modern engines it is made of light alloys, it completes the engine block from above. The cylinder head contains intake and exhaust channels, coolant channels, lubrication channels, valve seat rings, valve guides, valve journals, as well as holes for spark plugs or injectors and the combustion chamber. The cylinder head gasket between the engine block and the cylinder head keeps oil, coolant and air out and in.
Cylinders: pistons oscillate between bottom dead center (NMT) and top dead center (TDC): the working surfaces of the cylinders exactly match the diameter of the pistons in their diameter and then their surfaces are specially processed again (honed). They are either indirectly cooled by the cooling channels or, in the case of wetted cylinder liners, they are flushed directly by the coolant.
Pistons: oscillate in the cylinders and transmit the combustion pressure through the connecting rods to the crankshaft. The pistons are made of particularly light and heat-resistant light alloys. Their main elements are the bottom of the piston, the zone of rings with piston rings, the holes for the piston pin and the trunk part of the piston. The piston pin connects the piston to the connecting rod. Top piston rings (O-rings) seal the combustion chamber almost gas-tight from the crank mechanism. bottom ring (oil scraper piston ring) diverts excess lubricating oil from the cylinder walls to the crankcase (oil pan).
Connecting rod: connects the piston to the crankshaft Consists of a hole in the connecting rod (guides the piston pin), connecting rod stem, connecting rod base and connecting rod base cap (the connecting rod base and the connecting rod base cap cover the crank pin with bearing shells).
Crankshaft: converts vibration energy via connecting rod link (piston travel from TDC to BDC) into rotational energy (rotational movements). Modern crankshafts consist of a forged body that rotates at the main bearings of the engine block. Depending on the number of cylinders with a precisely defined offset (angular degree) two cheeks of the crankshaft lead to the crank pins (connecting rod journals). Focus crankshafts have five main bearings and four connecting rod bearings offset at an angle of 90'. Replaceable three-piece plain bearings are inserted into all bearing journals.
Valves: control the process of gas exchange in four-stroke engines (suction, compression, combustion, exhaust). In OHC-Endura engines, the valves are suspended «shoulder to shoulder» under the distributor. The DOHC-Zeteconn engines are suspended in a V-shape at a 42°angle below the camshafts. All moving parts in the cylinder head form the valve train.
Camshaft: opens and closes valves - depending on engine speed and piston position - at precisely defined intervals.
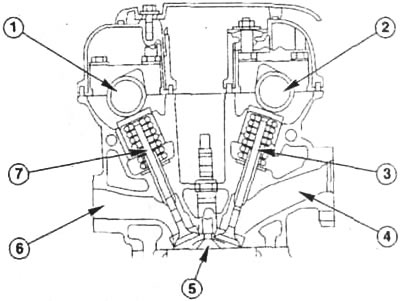
The camshaft drive of Ford OHC / DOHC engines is a toothed belt. 1 - exhaust camshaft, 2 - intake camshaft; 3 - inlet valve; 4 - inlet channel; 5 - combustion chamber in the form of a roof; 6 - outlet channel; 7 - exhaust valve.
Visitor comments