Four stroke principle
1. Suction (1st measure): The piston slides from TDC to BDC. The intake valve opens and the air-fuel mixture flows into the cylinder.
2. Compression (2nd measure): The piston slides from BDC to TDC and compresses the fresh air-fuel mixture that has been sucked in on its way. The intake and exhaust valves are closed.
3. Combustion (3rd measure): before TDC, the compressed air-fuel mixture is ignited by a spark of a spark plug, the mixture burns like an explosion, due to the increase in pressure, the piston is pressed to the BDC position. The connecting rod transfers energy to the crankshaft and causes it to rotate.
4. Push (4th measure): The inertial mass of the flywheel again moves the piston from BDC towards TDC. The exhaust valve is already open, so the burnt (spent) gases can escape into the exhaust system. In general, four cycles form gas exchange in a four-stroke engine.
In principle, a diesel engine operates on the same principle. On the intake stroke, it sucks in clean air, compresses it much more strongly, so at the end of the compression stroke, the injected fuel (diesel) from contact with hot air ignites independently, without ignition from an external source (ignition sparks). The rest of the gas exchange is then carried out in exactly the same way as a gasoline engine.
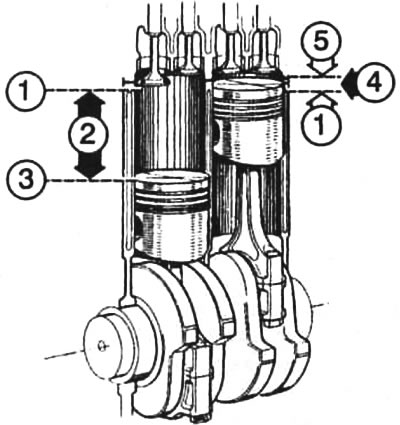
The working volume 2 extends from the top 1 to the bottom 3 dead center. Between the TDC, which in the right cylinder is just limited by the base of the piston, and the bulge of the cylinder head 5 is the combustion chamber 4
Displacement: the space that the pistons travel from BDC to TDC during their movement. The combustion chamber has no effect on the displacement. The working volume and the combustion chamber together form the volume of the cylinder.
Compression ratio: The ratio in which the fresh gas sucked in is compressed in the combustion chamber. The size of the combustion chamber has a direct effect on the compression ratio. The compression ratio indicates how much fresh gas at 100% filling (wide open throttle) must be in the combustion chamber at the time of ignition. Endura turbocharged diesel engines have a compression ratio of 19.4:1. Zetec-SEs operate at an 11:1 compression ratio, while E models compress fresh gas at a 10:1 ratio.
Visitor comments