If you want to drive economically, increase your speed slowly and always try to coordinate your speed with a gear that brings the engine speed close to maximum torque. In order to be able to combine torque and speed as smoothly as possible, the Focus uses a fully synchronized five-speed gearbox. Combined with the 1.6L Zetec-SE engine, Ford offers an electronically controlled four-speed automatic with overdrive and torque converter bypass clutch as an alternative (4F27E).
Traction conversion
To be able to easily increase speed from a standstill, the drive wheels need a lot of torque. But as you'll see from the power curves, below 1500 rpm, at least with petrol engines, there's still not enough torque: so using the 1st gear sluggish gear makes it easier to rev the engine smoothly and drive the Focus. When the fourth and fifth gears are engaged, the opposite happens: in both gears, the conversion to acceleration becomes effective. Compared to the speed of the drive wheels, the engine rotates slower in overdrive gears. In other words: the gearbox adjusts the engine speed to the desired speed of the drive wheels.
During a gear shift, the engine is disconnected from the gearbox - clutch
Every time you start driving or changing gears, the power flow between the engine and gearbox is interrupted for a short time. In manual transmission vehicles, the clutch does this. It allows you to gently move off and change gears without jerks by equalizing the different speeds of the crankshaft and the drive shaft of the gearbox. The interconnection of the planetary gears of an automatic transmission functions more complexly: in this case, each shift is carried out without interruption in traction.
Torque converter - transmits torque to the gearbox hydraulically
In an automatic transmission, instead of a conventional friction clutch, the start of movement and gear changes are coordinated by a hydraulic torque converter. In the Focus, this is done by adjusting six solenoid valves that control the automatic transmission from a common housing. The torque converter not only works extremely comfortably, but also without mechanical wear.
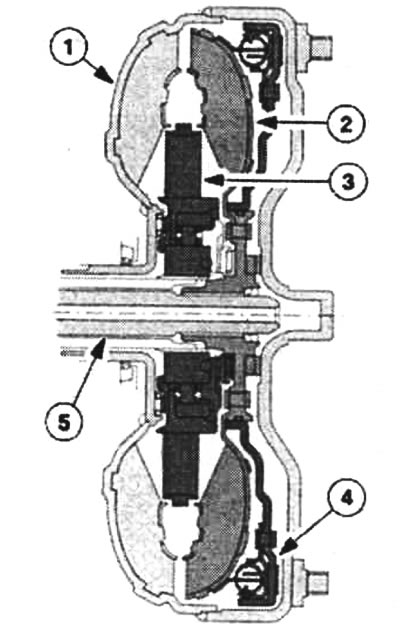
Torque Converter with Torque Converter Bypass Clutch: 1 - converter housing and pump wheel; 2 - turbine wheel; 3 - guide wheel; 4 - clutch with torque converter shunting; 5 - input shaft of the gearbox.
The last link before the drive wheels is the final drive
On the way to the drive wheels, the engine torque passes the last link - the final drive. Its task is to slow down the speed coming from the gearbox, i.e. increase the torque and evenly distribute it to the drive wheels.
Visitor comments