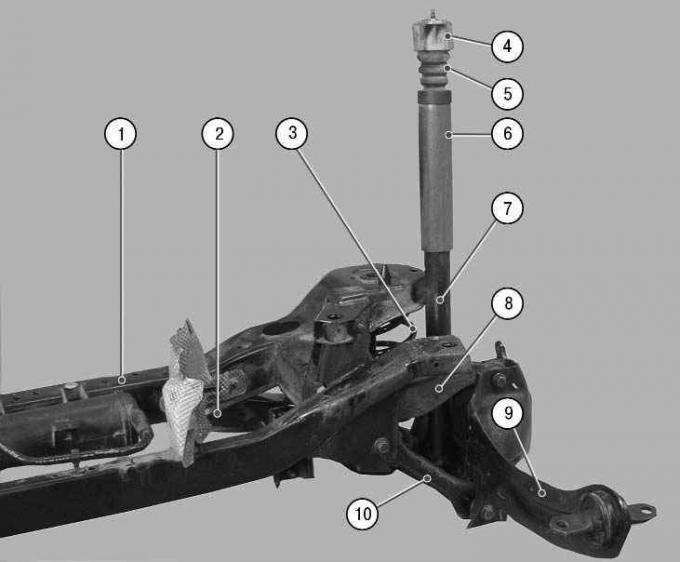
Pic. 7.2. Rear suspension of cars with sedan and hatchback bodies: 1 - rear suspension cross member; 2 - rear lower rear suspension arm; 3 – a spring of a back suspension bracket; 4 – an arm of fastening of a shock-absorber of a back suspension bracket; 5 – compression buffer; 6 – a protective casing of a shock-absorber of a back suspension bracket; 7 - rear suspension shock absorber; 8 - the upper arm of the rear suspension; 9 – trailing arm of the rear suspension; 10 - front lower rear suspension arm
Rear suspension of Ford Focus II cars with sedan and hatchback bodies (pic. 7.2) independent, multi-link spring (three transverse and one longitudinal on each side), with telescopic shock absorbers and anti-roll bar.
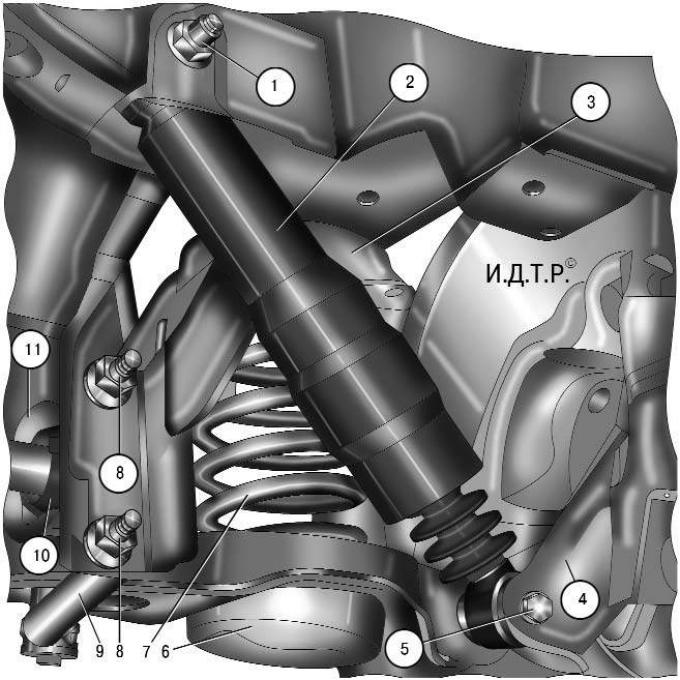
Pic. 7.3. Rear suspension of cars with station wagon: 1 - shock absorber upper mounting bolt; 2 - shock absorber; 3 - cross member of the rear suspension; 4 – trailing arm of the rear suspension; 5 – a bolt of the bottom fastening of the shock-absorber; 6 - rear lower arm of the rear suspension; 7 - spring; 8 – nuts of bolts of fastening of a bracket of the stabilizer of cross-section stability; 9 – a bar of the stabilizer of cross stability; 10 – a pillow of a bar of the stabilizer of cross-section stability; 11 - bracket stabilizer bar
The rear suspension of station wagon cars is similar in design to the suspension of sedan and hatchback cars and differs only in the shock absorber mounting (pic. 7.3).
The camber angle of the rear wheels is set by design and is not adjustable in operation. According to the camber angle, you can only control the condition of the rear suspension (cm. «Checking and adjusting wheel alignment»). The convergence of the rear wheels is regulated by the bolts of the rear lower arm, made in one piece with the eccentrics.
Visitor comments