Fuel system
2. An electric fuel pump located inside the fuel tank pumps fuel into the fuel line from which it flows to the fuel injectors. The fuel filter is installed between the fuel pump and the fuel line. The pressure regulator controls the pressure in the system depending on the vacuum in the intake tract. From the fuel line, fuel is injected through four fuel injectors into the intake ports located directly above the intake valves. The system also includes a cold fuel jet device surrounding each fuel injector that is used to improve warm engine starting.
3. Dosing of fuel by fuel injectors is carried out under the control of the electronic control unit of the BZU. This device receives signals from the crankshaft position / engine speed sensor and the camshaft position sensor and, depending on this, activates the fuel injectors individually in accordance with the firing order of the cylinders (sequential injection) to achieve low fuel consumption and emission levels.
Air intake system
4. The air intake system includes an air filter housing, an air mass meter, an intake air duct, and a throttle body. The flow meter, which uses an incandescent filament as a sensitive element, outputs to the BEU a signal of varying voltage in accordance with the volume of air entering the engine. Another sensor installed in the air flow meter monitors its temperature. Based on these signals, the BEU calculates the mass of air entering the engine.
5. The throttle valve installed inside the body is controlled by the gas pedal. When it opens, the amount of air entering the system increases. The more the throttle potentiometer is moved, the higher the signal level of the air mass meter. In accordance with this, the BEU opens each nozzle for a longer time, due to which the amount of fuel entering the inlet windows increases.
Electronic control system
6. Electronic engine management system (EEC-IV and EEC-V) controls the fuel injection system, as well as other engine subsystems. She gets a signal (s) from sensors that monitor various parameters such as intake air mass and temperature, coolant temperature, engine position and speed, acceleration/deceleration, exhaust oxygen content. Based on these signals, the system determines the injection interval required to achieve the optimum air/fuel ratio. These sensors and relays controlled by the system are located in different places in the engine compartment.
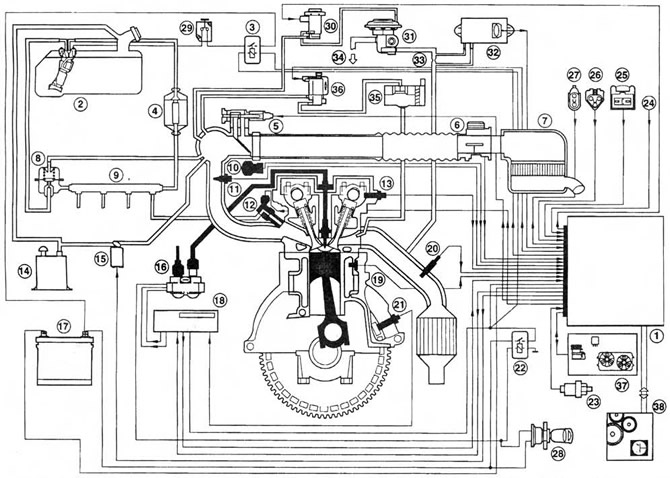 Pic. 12.6,a Engine control system - fuel injection, ignition and emission control subsystems are shown
Pic. 12.6,a Engine control system - fuel injection, ignition and emission control subsystems are shown
1. BEU (electronic control device)
2. Fuel pump/fuel gauge sensor
3. Fuel pump relay
4. Fuel filter
5. Idle control valve
6. Air flow meter
7. Air cleaner assembly
8. Fuel pressure regulator
9. Fuel line
10. Throttle Potentiometer
11. Intake air temperature sensor
12. Fuel injector
13. Camshaft position sensor
14. Carbon adsorber
15. Canister purge valve
16. Ignition coil
17. Battery
18. Ignition module - removed from the BEU (only for models with automatic transmission)
19. Coolant temperature sensor
20. Oxygen sensor
27. Crankshaft position/speed sensor
22. Supply voltage relay
23. Pressure sensor in the hydraulic steering system
24. Air conditioning compressor clutch solenoid
25. Octane switch connector
26. Self-diagnosis connector for Ford STAR diagnostic tester
27. Self-diagnosis connector for FDS 2000 diagnostic tester
28. Ignition switch
29. Fuel cut switch
30. Exhaust gas recirculation solenoid valve
31. Exhaust gas recirculation valve
32. Exhaust pressure difference sensor of the exhaust gas recirculation system
33. Place for measuring the pressure difference of the exhaust gas recirculation system
34. To the intake manifold
35. The filter housing of the afterburning system
36. The solenoid valve of the afterburning system
37. Air conditioner/electric fan control unit
38. Automatic transmission control system (in the presence of)
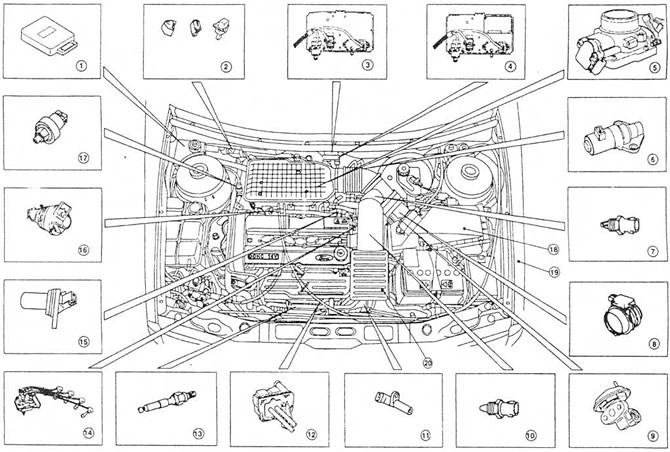 Pic. 12.6, b Location of the main components of the fuel injection, ignition and emission control subsystems on models with 4-cylinder engines
Pic. 12.6, b Location of the main components of the fuel injection, ignition and emission control subsystems on models with 4-cylinder engines
1. BEU (electronic control device)
2. Connectors for self-diagnosis, diagnostics and maintenance (from left to right)
3. Support bracket for components located on the bulkhead of the engine compartment (manual transmission, shown from left to right) - solenoid valve of the exhaust gas recirculation system, solenoid valve of the afterburning system, exhaust gas pressure difference sensor of the exhaust gas recirculation system
4. Support bracket for components located on the bulkhead of the engine compartment (automatic transmission, shown from left to right) - EGR solenoid valve, post-combustion solenoid valve, exhaust gas recirculation system differential pressure sensor, and ignition module located at the top
5. Throttle body together with potentiometer
6. Idle control valve
7. Intake air temperature sensor
8. Air flow meter
9. Exhaust gas recirculation valve
10. Coolant temperature sensor
11. Crankshaft Position/Speed Sensor
12. Filter housing of the afterburning system
13. Oxygen sensor
14. High voltage coil and spark plug wires
15. Camshaft position sensor 1B Fuel injector (And)
17. Pressure sensor in the hydraulic steering system
18. Air cleaner assembly
19. Air inlet and resonators - under the front left wing
20. Resonator
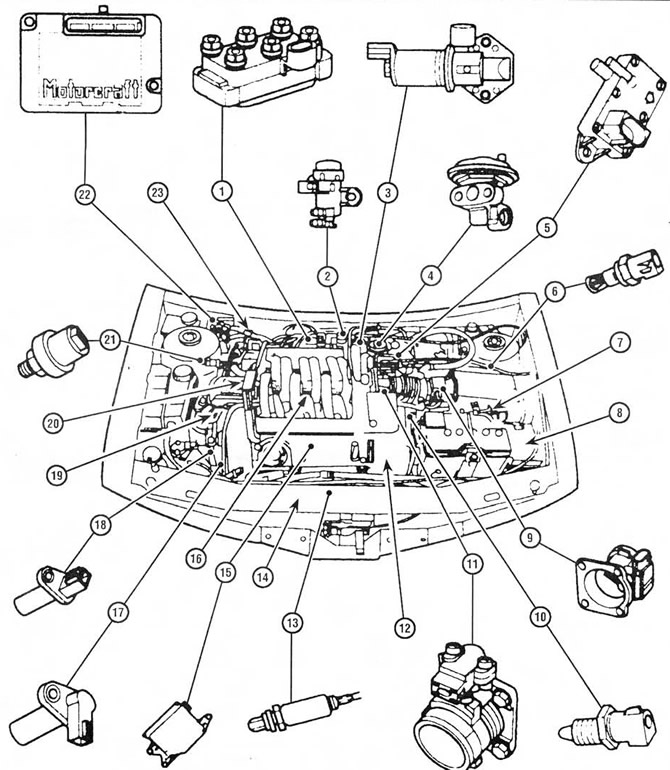 Pic. 12.6, in the Location of the main components of the fuel injection, ignition and emission control subsystems on models with V-shaped 6-cylinder engines
Pic. 12.6, in the Location of the main components of the fuel injection, ignition and emission control subsystems on models with V-shaped 6-cylinder engines
1. Ignition coil
2. Electronic vacuum regulator
3. Idle air control valve
4. RVG system valve
5. Electronic differential pressure sensor
6. Intake air temperature sensor
7. Air cleaner
9. Mass air flow meter
10. Coolant temperature sensor
11. Housing and throttle position sensor
12. Coolant pump drive belt cover
13. Heated oxygen sensor
14. Front catalytic converter (rear mounted on the exhaust manifold of the rear block head)
15. Air intake control unit through the intake manifold
16. Upper section of the intake manifold
17. Camshaft position sensor
18. Crankshaft position sensor
19. Engine hydraulic mount
20. Right engine mount
21. Pressure sensor in the hydraulic steering system
22. Power control module or electronic control device
23. Octane switch
7. In the event of a sensor failure, a backup circuit is activated to provide control until the failure is corrected.
Electronic control unit (BEU)
8. It is the main component of the engine management system and controls the fuel injection, ignition and emission control subsystems. The BEU also controls the electric radiator fan, air conditioning system and automatic transmission (depending on performance).
Mass air flow meter
9. It is based on an incandescent filament, which outputs a continuously changing (analog) voltage signal according to the mass of air entering the engine.
Crankshaft Position/Speed Sensor
10. This is an induction pulse generator mounted on the cylinder block (4 cylinder engines) or on the timing cover (V-shaped 6-cylinder engines). It is designed to scan the ridges located between the 36 holes on the flywheel/faceplate (4-cylinder engines) or on a disc mounted on the crankshaft (V-shaped 6-cylinder engines). When the protrusion is against the tip of the sensor, the latter generates a signal, on the basis of which the ECU determines the speed of the engine.
11. Protrusion between the 35th and 36th holes (90°before TDC) is absent, and the pause upon receipt of the signal is perceived by the BEU as a reference mark corresponding to the position of the crankshaft.
Camshaft position sensor
12. On 4-cylinder engines, it is located on the head of the block at the rear left and is bolted. The sensor responds to a protrusion located on the intake camshaft. On V-shaped 6-cylinder engines, the sensor is located on the front head of the block on the right. The sensor responds to a protrusion located on the intake camshaft of the front head of the block. It works in the same way as the crankshaft position/speed sensor. As a result, the BEU has a reference point (46°after TDC for cylinder #1) to determine the firing order of the cylinders and turn on the fuel injectors in the appropriate sequence.
Coolant temperature sensor
13. The sensor is threaded on the top of the thermostat housing (4 cylinder engines) or on the connecting pipe of the cooling system (V-shaped 6-cylinder engines). This is a thermistor, that is, a semiconductor device whose resistance decreases as its temperature increases. It gives out to the BEU a continuously changing (analog) voltage signal according to coolant temperature. The obtained information is used by BEU to refine the calculations in order to ensure the ideal ratio of the components of the air-fuel mixture.
Intake air temperature sensor
14. On 4-cylinder engines, the sensor is installed on the thread on the underside of the intake air duct resonator (release models before 1997) or in the intake duct (release models since 1998). On V-shaped 6-cylinder engines, the sensor is installed in the air cleaner cover. The sensor is based on a thermistor, the signal of which changes depending on the temperature of the air entering the engine. It is also used to refine the calculations performed by the BEU when determining the dose of injected fuel in order to achieve the ideal ratio of the components of the air-fuel mixture.
Throttle Potentiometer
15. The component is installed on the end of the throttle shaft. Depending on the value of the damper opening, it outputs an analog voltage signal to the BEU. Due to this, the BEU registers the impact of the driver with the chain for determining the dose of fuel injected into the engine.
Speedometer sensor
16. The sensor is installed on the speedometer drive. It is a pulse generator based on the Hall effect. The sensor generates a sequence of pulses in the BEU depending on the speed of the vehicle. Based on this information, the ECU controls functions such as fuel cut-off after engine shutdown. Information from this sensor also feeds into the on-board computer, active suspension system and constant speed device (depending on performance).
Steering hydraulic pressure sensor
17. The sensor is installed on the thread on the steering hydraulic discharge pipe. It has normally closed contacts that open when the system reaches the regulated pressure. Receiving this signal, the BEU increases the idle speed to compensate for the additional load on the engine.
Air conditioning system
18. To provide information about the operation of this system, two pressure sensors and a compressor clutch solenoid are connected to the BEU. The BEU can increase the idle speed or, if necessary, turn off the air conditioning system so that the dynamic qualities of the car do not deteriorate. See chapter 3. Please note that diagnosing and repairing this system is the 8 responsibility of dealers.
Idle control valve
19. The valve maintains a constant idle speed by changing the amount of air entering the engine through the auxiliary air channel. The valve is activated by the ECU signal.
Automatic transmission sensors
20. In addition to the components that transmit the driver's influence on the transmission, it also has a speed sensor, a fluid temperature sensor (built into solenoid valve) and selector position sensor. All these sensors are connected to the ECU, which controls the transmission through a solenoid valve. See chapter 7B.
Oxygen sensor
21. A sensor installed in the exhaust system provides the BEU with a continuous feedback signal. This allows you to adjust the composition of the mixture to ensure optimal operation of the catalytic converter. See Chapter 4B.
Windshield defroster solenoid
22. When the windshield defroster is turned on, the solenoid allows additional air into the intake manifold to compensate for the extra load on the alternator.
Visitor comments