To disassemble the engine, you will need a special tool: a setting gauge for adjusting the camshafts, an insert for a multi-pointed wrench for loosening and tightening the nuts. If it is necessary to remove the crankshaft or connecting rods, a Plastigage plastic rod is required to measure bearing clearances.
When completely disassembling the engine, observe the following sequence (gearbox removed from engine flanges):
Pre-May 1998 production engines
- lay the engine on the workbench, taking into account the described preparatory work;
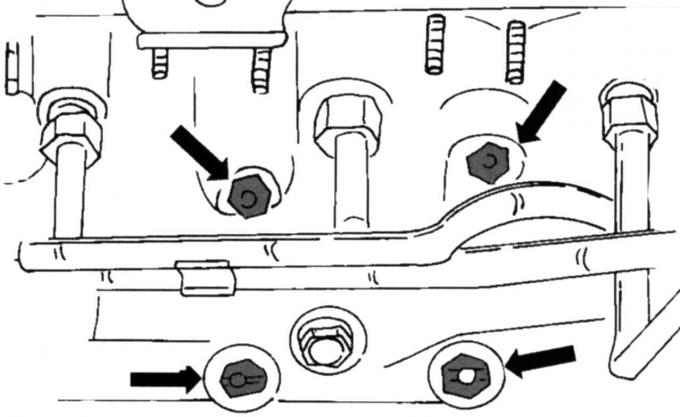
Pic. 40. Mounting points of the catalytic converter
- on a 2 liter engine, unscrew the catalytic converter from the exhaust manifold (pic. 40);
- disconnect all multi-pin connectors (engine wiring harness, throttle control, camshaft position sensor); other connectors can be found on the ignition coil and interference suppression capacitor, as well as for the coolant temperature sensor (above the plug for the ignition coil). Disconnect the plug connector on the generator;
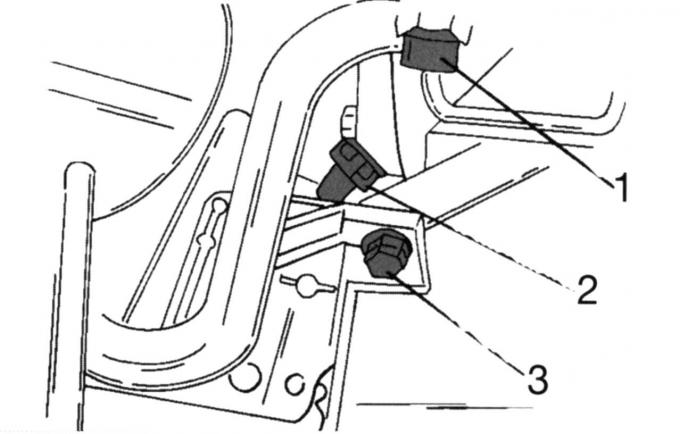
Pic. 41. The position of the plug-in blocks: 1, 2 - plug-in blocks; 3 - screw
- remove multi-pin plugs 1 and 2 (pic. 41) respectively the temperature sensor for the remote thermometer and the crankshaft position sensor. Loosen screw 3;
- Turn away three screws and remove the thrust bearing of a power shaft. In the immediate vicinity of it, unscrew the oil membrane switch;
- Unscrew the main engine wiring harness from the intake manifold. It is fortified in three places. Loosen the alternator mounting screws and remove it. The adjacent belt roller can also be removed. After removing the generator, remove the suspension bracket and unscrew the bracket of the engine mount;
- Remove the valve of system recirculation of the fulfilled gases and consolidation. Unscrew the fastening of the Pulse-Air system in this area;
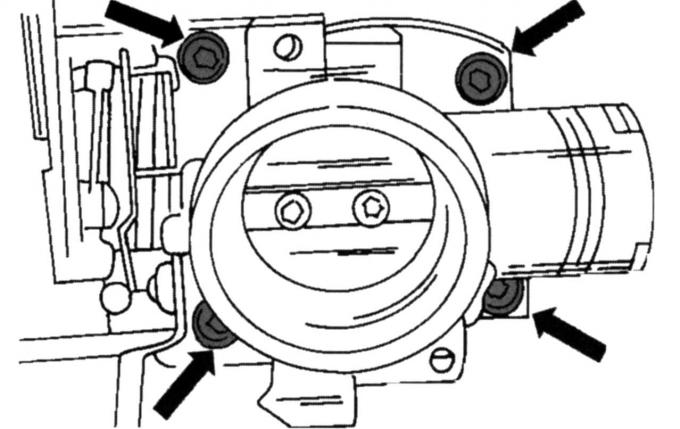
Pic. 42. Throttle body attachment points
- unscrew the throttle body (pic. 42);
- Disconnect the engine vent hose from the intake manifold pipe and unscrew the four nuts and two screws securing the manifold;
- Remove an inlet collector;
- install the engine on the mounting stand, drain the engine oil and unscrew the oil filter;
- Remove the heat shield with fastener and coolant hose with pipe;
- unscrew the compressor consoles (if installed) and auxiliary steering pump;
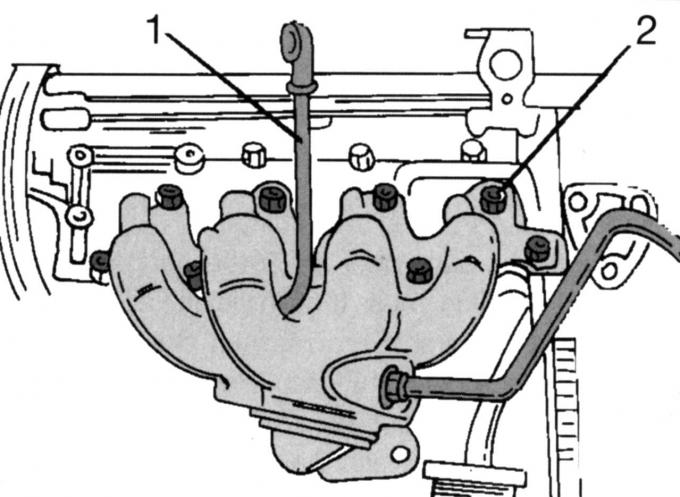
Pic. 43. Mounting the exhaust manifold on one side of the engine: 1 - oil dipstick; 2 - manifold fastening nuts
- remove the oil dipstick 1 (pic. 43), unscrew the nine nuts 2 and carefully remove the exhaust manifold with the Pulse-Air system;
- remove the spark plug caps, unscrew the ignition coil holder (three screws) and thermostat housing (three screws);
- remove the crankcase ventilation pipe, remove the three fan screws and remove the fan;
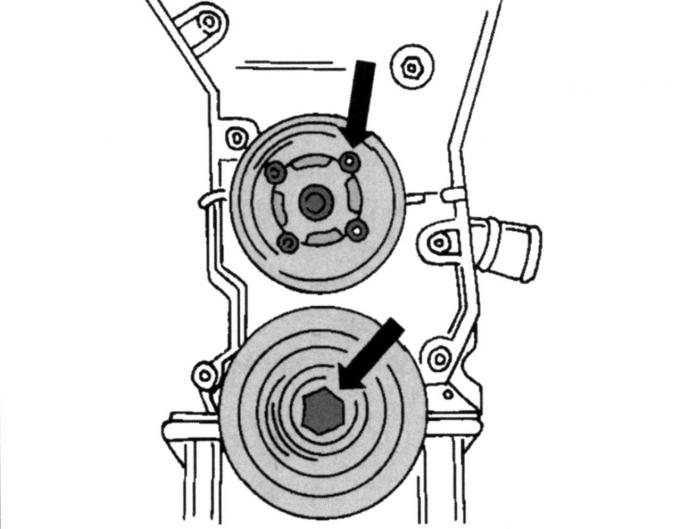
Pic. 44. Fluid pump and crankshaft pulleys
- Remove the belt pulley of the liquid pump and crankshaft (pic. 44). When unscrewing the latter, the crankshaft must be kept from turning;
- unscrew the protective cover of the toothed drive belt on the front side;
- holding the flywheel from turning, unscrew the clutch. Remove the driven disk. Remove the automatic transmission torque converter drive disc in the same way;
- Turn out spark plugs;
- Remove the toothed drive belt, as described below for this engine in the relevant subsection;
- Remove the released crankshaft drive gear. On the outer side of the gear disk there is an inscription «FRONT». Behind it is a thrust washer. Remove it from the end of the crankshaft;
- Remove both camshafts and cylinder head;
- Remove a cover of a head of the block of cylinders and consolidation;
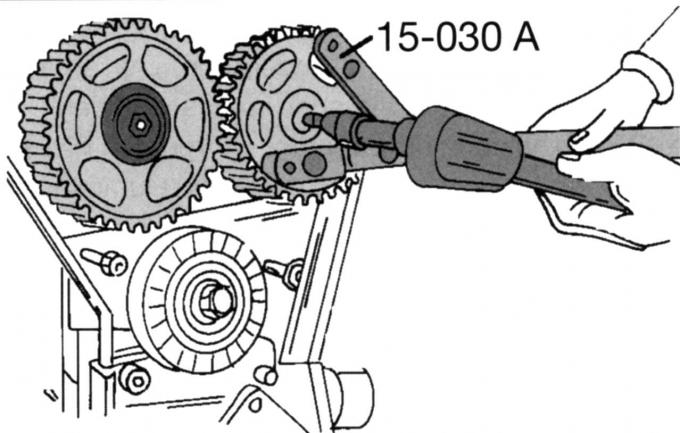
Pic. 45. Camshaft gear holding tool
- Loosen the screws securing the camshaft pulleys. In this case, the camshafts will rotate, they must be kept from turning (pic. 45). If no special tool is available, insert a drift into one of the holes and carefully lock it against the cylinder head. Remove both toothed pulleys, marking their belonging;
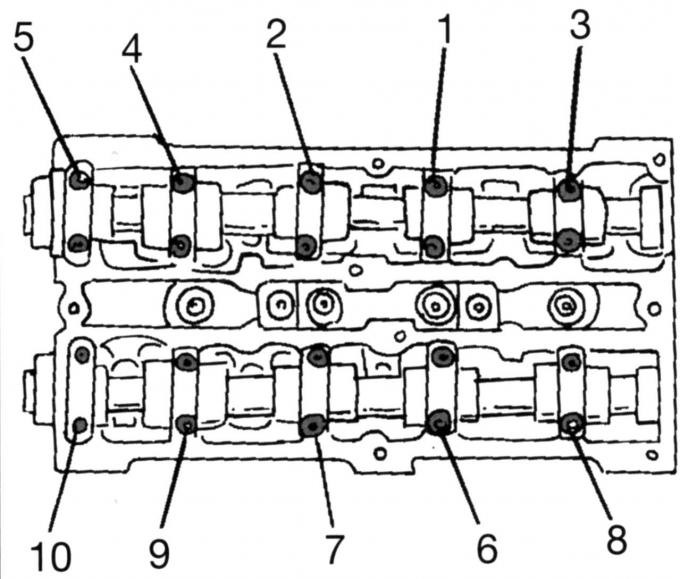
Pic. 46. The sequence of loosening the camshaft bearing caps
- Remove camshafts. To prevent the shafts from deforming, loosen the bearing caps in a certain sequence (pic. 46). Loosen the nuts of the bearing caps in the sequence shown by half a turn until they are free and can be unscrewed by hand. Label the covers and remove them one by one. Carefully remove both camshafts and remove radial sealing rings;
- remove the hydraulic pushers one by one and set them aside in the sequence required for installation, or mark them;
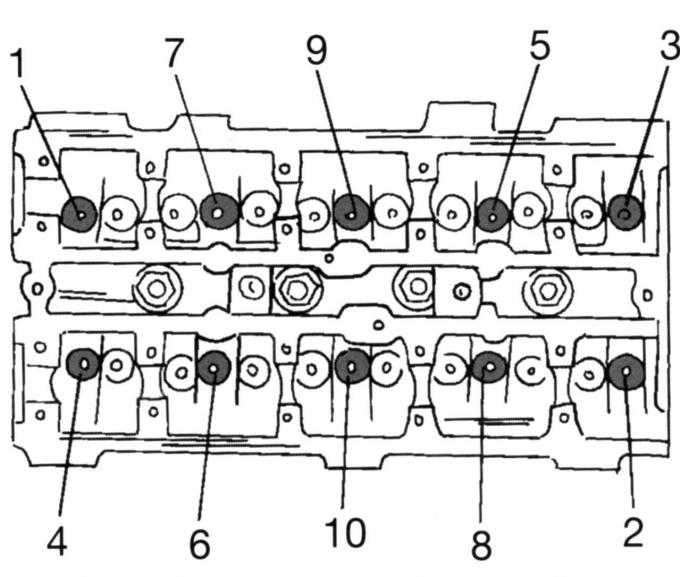
Pic. 47. The sequence of loosening the cylinder head screws
- Remove the cylinder head assembly. To do this, unscrew the screws in the sequence shown in fig. 47. To do this, you will need a wrench with a multi-sided socket head so as not to damage the screw heads. After removing the oil dipstick tube, remove the cylinder head (if necessary, help with a rubber mallet) and put it on two wooden blocks;
- turn off the liquid pump (four screws);
- Align the engine so that the oil pan is at the bottom and unscrew it. Thus, the oil sludge will remain in the bath and will not drain into the cylinder;
- on the reverse side of the engine, unscrew the holder of the crankshaft position sensor and the cover with the oil sealing ring (four screws). The oil seal ring can be immediately removed from the cover;
- unscrew the oil suction strainer from the inside of the crankcase. The oil line shield is now accessible, it can be removed after unscrewing the four nuts;
- Turn away six screws and remove the oil pump;
- turn the crankshaft (at the edge of the flywheel) so that all pistons stand approximately in the middle of the stroke, and with a scraper, carefully scrape off the carbon deposits from the ring on the upper side of the cylinder bores, without damaging the cylinder bores;
- in turn turn away from rods of a cover of bearings. Lightly hit the cover with a rubber mallet and remove it together with the bearing shell. Usually caps and connecting rods are marked with numbers from 1 to 4, but it is necessary to check if these numbers are visible. The cylinder number is respectively stamped on the connecting rod and bearing cap in opposite places;
- Push the pistons with connecting rods from below through the cylinders. Accordingly, two pistons should be at bottom dead center (NMT), to facilitate removal. Bearing caps and liners are best screwed back onto the matching connecting rod to keep them together;
- the flywheel is held on by six screws and can be detached. When turning off the flywheel, the crankshaft must be locked. This is best done by wedging a wooden block into the inside of the crankcase so that it is between the crankshaft cheek and the crankcase wall, and the shaft is clamped;
- Turn away screws of fastening of covers of radical bearings of a cranked shaft, having a little loosened each screw;
- take out screws and covers of bearings with loose leaves. Label each cap and insert (e.g. colored labels), so that they can be installed again in their original place;
- carefully remove the crankshaft from the bearings and put it in a clean place;
- take out the bearing shells located in the crankcase and mark them so as not to confuse them, put them aside to other bearing shells;
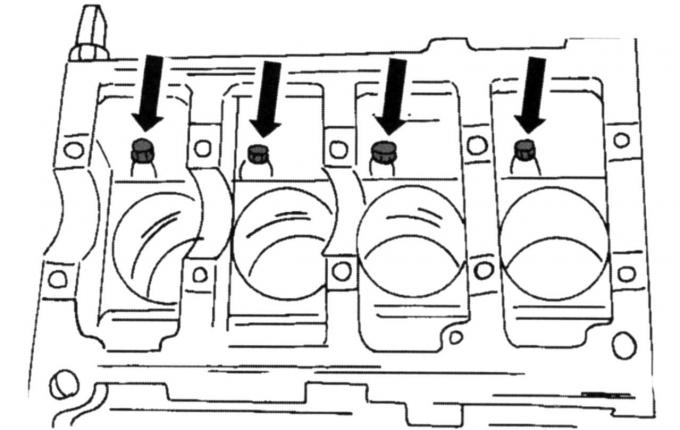
Pic. 48. The position of the oil nozzles in the cylinder block
- in the places shown in Fig. 48, there are oil nozzles for piston cooling. They can also be removed;
May 1998 release engines
- having completed the described preparatory work, install the engine on the workbench;
- Disconnect the wire plugs from the camshaft position and coolant temperature sensors. Disconnect the wires from the ignition coil;
Pic. 49. The location of the plug-in blocks for the oil pressure switch and the knock sensor of the fuel
- disconnect the plugs from the oil pressure switch and the fuel knock sensor (pic. 49);
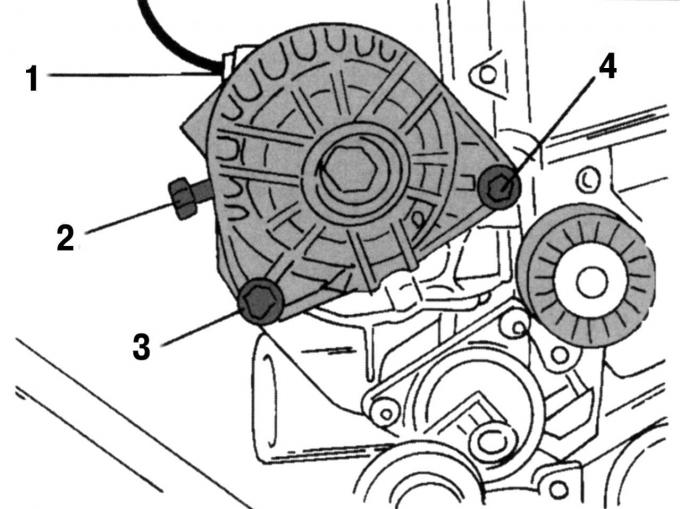
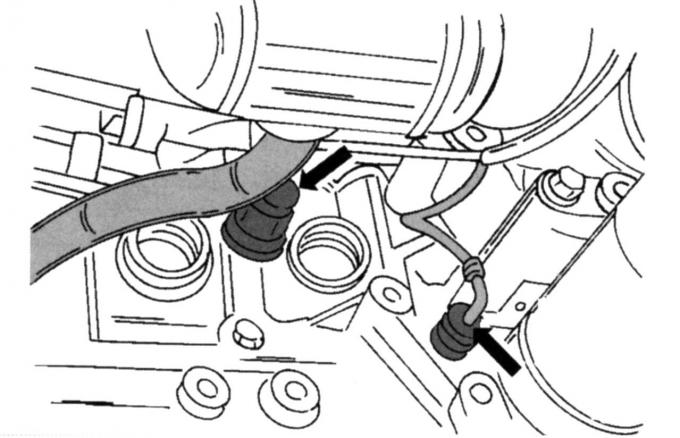
Pic. 50. Generator mount: 1 - plug; 2 - cable; 3, 4 - screws
- Remove the generator. To do this, disconnect the plug 1 (pic. 50), current-carrying cable 2, remove screw 4 and unscrew screw 3;
- Disconnect the plug from the solenoid valve mounted on the intake manifold, unscrew the seven screws and two nuts and remove the intake manifold;
- Remove the alternator carrier, oil filter, knock sensor and oil pressure switch on the intake side of the engine;
- unscrew the console for the auxiliary steering pump and the air conditioning compressor at the front (if it is installed);
- Remove details of crankcase ventilation. To do this, remove and remove the three screws;
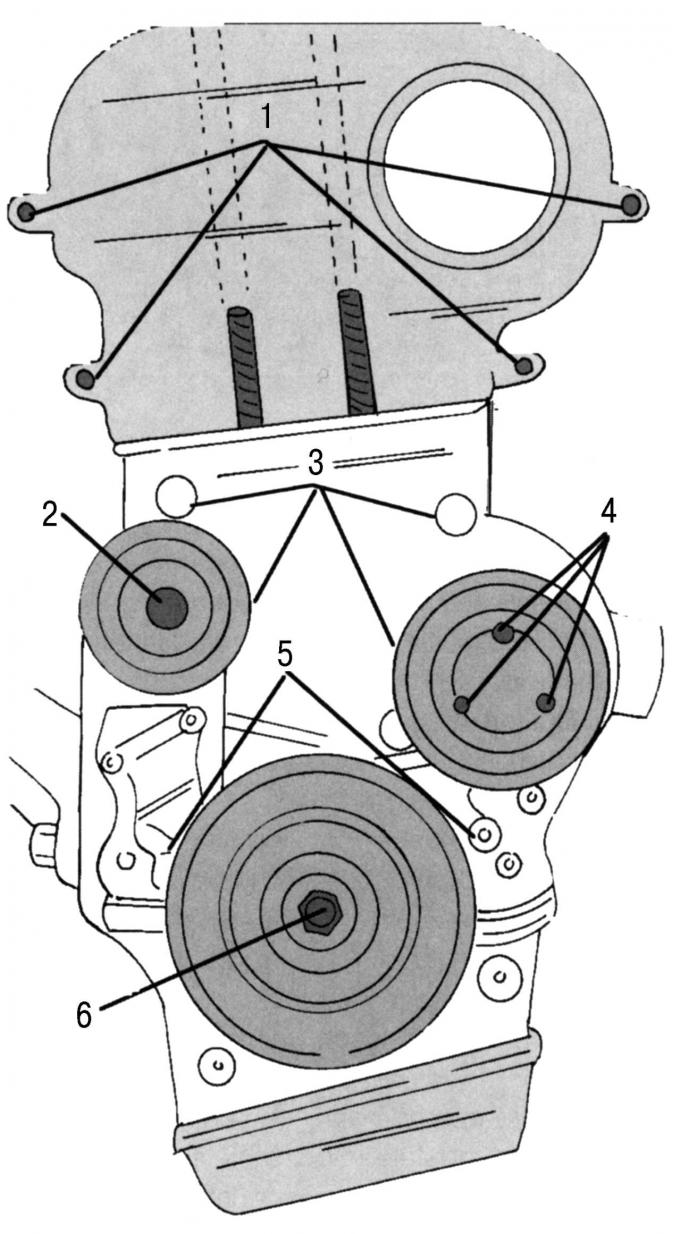
Pic. 51. Removing parts on the front side of the engine: 1 - top cover; 2 - running roller; 3 - middle cover; 4 - water pump pulley; 5 - cover; 6 - crankshaft pulley
- Remove a protective casing of a gear driving belt. Before removing the bottom cover, remove the fluid pump pulley 4 (pic. 51), poly V-belt roller 2 and middle cover 3 together with engine mount. After that, remove the top cover 1, the crankshaft belt pulley 6 and the cover 5. To loosen the pulley screw, hold the crankshaft from turning;
- Remove the cap from the cylinder head. First, disconnect the high voltage wires from the spark plugs. When doing this, do not pull on the cables, but on the plugs. Loosen the cover screws at the top of the engine and remove the spark plugs;
- remove a toothed drive belt, as described in the relevant subsection, for this engine, and unscrew the liquid pump. The belt drive can be equipped with a running roller for a toothed drive belt;
- loosen the fastening screws of both camshaft pulleys, keeping the shafts from turning. The clamp shown in fig. 45 is best suited for this purpose. If not, insert a drift into one of the holes and carefully lock it against the cylinder head. Remove both pulleys, marking their belonging;
- Remove camshafts. In order not to deform the shafts, loosen the bearing caps in a certain sequence (see fig. 46). Accordingly, loosen the bearing cap nuts in the sequence shown by half a turn until they can be unscrewed by hand. Label the covers and remove them one by one. Carefully remove both camshafts and remove radial sealing rings;
- remove the poppet pushers one by one and set them aside in the sequence required for installation, or mark them accordingly;
- Remove the cylinder head assembly. To do this, unscrew the screws in the sequence shown in fig. 47. To do this, you will need a wrench with a multi-sided socket head so as not to damage the screw heads. After removing the oil dipstick tube, remove the cylinder head (if necessary, help with a rubber mallet) and put it on two wooden blocks;
Note: The cylinder head screws on these engines can only be used twice, so mark them with one or two punch strokes. If the screws already have two punch notches, they have already been used twice.
- Align the engine so that the oil pan is at the bottom and unscrew the oil pan. Thus, the oil sludge will remain in the bath and will not drain into the cylinders.
- on the reverse side of the engine, unscrew the holder of the crankshaft position sensor and the cover with the oil sealing ring (four screws). The oil seal ring can be immediately removed from the cover;
- unscrew the oil suction strainer from the inside of the crankcase. Thus, the lower half of the crankcase is separated from the cylinder block;
- Turn away six screws and remove the oil pump;
- turn the crankshaft (at the edge of the flywheel) so that all pistons stand approximately in the middle of the stroke, and with a scraper, carefully scrape off the carbon deposits from the ring on the upper side of the cylinder bores, without damaging the cylinder bores;
- in turn turn away from rods of a cover of bearings. Hit the cover lightly with a rubber mallet and remove the cover together with the bearing shell. Usually caps and connecting rods are marked with numbers from 1 to 4, be sure to check if these inscriptions are visible. The cylinder number is respectively stamped on the connecting rod and bearing cap;
- Push the pistons with connecting rods from below through the cylinders. Two pistons should be at BDC to facilitate removal. Bearing caps and liners are best screwed back onto the matching connecting rod to keep them together;
- Disconnect the clutch;
- the flywheel is held on by six screws, it can be unscrewed by locking the crankshaft. This is best done by wedging a wooden block into the inside of the crankcase so that it is between the crankshaft web and the crankcase wall, and the shaft should be clamped;
- Turn away screws of fastening of covers of radical bearings of a cranked shaft, having a little loosened each screw;
- Remove the screws and bearing caps with half bearing shells. Label each lid and insert appropriately (e.g. colored labels), to then install in the original place;
- carefully remove the crankshaft from the bearings and put it in a clean place;
- remove the bearing shells located in the crankcase and mark them accordingly;
- in order not to confuse them, set them aside with other bearing shells.
Visitor comments