Anti-lock braking system (ABS), emergency brake system (EBA), traction control (TCS), electronic brake force distribution (EBD), electronic stabilization program (ESP)
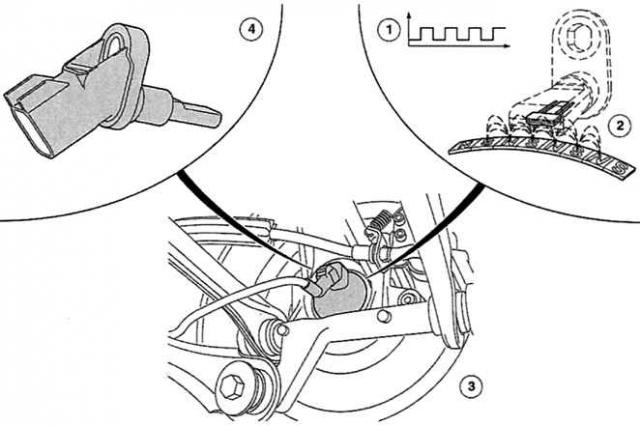
ABS and TCS increase active driving safety, EBD replaces mechanical brake force regulator and EBA (option) increases the initial braking pressure during an emergency braking process. The ABS function retains full control ability under full braking, TSC improves directional stability when accelerating on bumpy roads. Electronic brake force distribution has become another active safety component in modern braking configurations (EBD) and emergency brake system (EBA). EBD becomes active before ABS and improves braking stability by electronically fine-tuning rear wheel slip. The emergency brake system determines, depending on the speed with which the brake pedal was pressed, whether full braking or completely normal braking occurs. If the icon is on «full braking», EBA increases the brake pressure automatically to the maximum possible value - even when the brake pedal is not yet fully depressed. The braking process assistant is thus an assistant in shortening the braking distance – perhaps by a decisive few centimetres. The anti-lock braking system used in the Mondeo contains an electronic and hydraulic control unit (HECU). Both systems are enclosed in one common aluminum case. HECU is used to accurately register wheel speeds, a separate sensor is installed for each wheel: EBD and TCS use the same signals. The HECU operates with eight solenoid valves, a hydraulic DC motor driven pressure pump and two low pressure accumulators. In the Mondeo, all wheels can be adjusted individually up to a speed of 120 km/h. on the rear axle as «sample» the wheel that is first suitable for blocking is used. When system errors occur, ABS, EBA, EBD and TCS are turned off - the braking process continues to function without its own «assistants», like a normal braking system. Faults in the system are recognized by the ABS warning light: it no longer goes out after a corresponding self-test, but lights up permanently. The Mondeo ABS system is fully diagnosable, fault codes are archived in permanent memory on request. In addition, Ford supplies the Mondeo with an ESP system on request.
Brake power dosing - electronic dual circuit pump
The braking energy in the system is distributed by means of an electronic dual-circuit pump. Each of the four individual control channels is associated with a pair of solenoid valves (one intake and one exhaust valve). Intake valves are usually open and have switch ports (small orifice for fine control of low flow rates during braking contact, large orifice for minimum flow resistance during normal braking).
Braking Process Analysis - EVA
EVA already at the stage of pressing the brake pedal recognizes whether such pressing is a normal procedure or caused by a panic situation on the road. In a situation «panic» EVA increases the initial brake pressure automatically up to the limit of wheel blocking. It also helps «inexperienced» the driver of his Mondeo in critical situations to brake with the theoretically shortest stopping distance. If the pressure on the pedal drops to the programmed value, then EBA switches control only to the driver himself. Mondeo emergency braking assistant built into NBZ unit (GTZ) / brake booster.
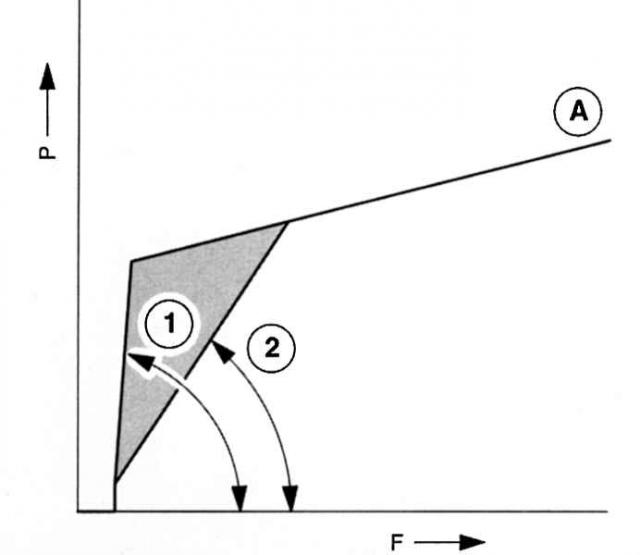 Depends on the speed at which the brake pedal is depressed: initial brake pressure. 1 - with EVA,
|
ABC Operations Control - HECU
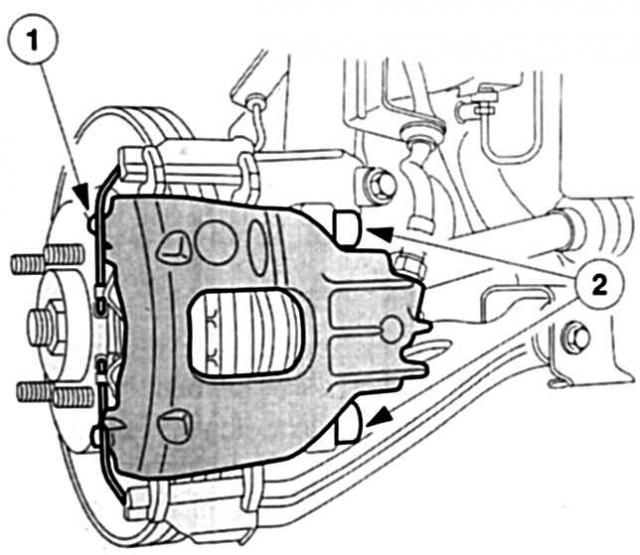
HECU controls the operation of the ABC, calculates the speed depending on the signals from the wheel speed sensors. Monitors all electrical components and records failure parameters. With the ignition on, the system performs a HECU-initiated self-test before driving. While driving, all electrical connections are under the watchful eye of the HECU. This process is carried out taking into account priorities, as well as checking the patency of individual electrical circuits. At the same time, the solenoid valves are regularly tested for function: the system generates an electrical impulse for this. Possible faults are quickly and specifically read out at the Ford station using the WDS tester. The diagnostic connector for this is located on the left under the instrument panel.
Rear wheel slip limiter - EBD
EBD limits, milliseconds before the main system is activated, rear wheel slippage. It constantly compares the slip on the rear and front wheels and doses or distributes the braking force accordingly. The operation of the EBD is usually imperceptible, its technology - regardless of the state of the vehicle's load - implements a minimum braking distance. In addition, EBD replaces the conventional brake force regulator in the system.
Active up to 50 km/h – TCS
The TCS is integrated into the Mondeo ABS system along with two shut-off solenoid valves and two hydraulic intake valves. This system, depending on the need, is active up to a border of 50 km/h. It can be used to benefit from sudden accelerations from a standstill and, in particular, when cornering, as well as the steering of your Mondeo: if the TCS detects a slip of the front wheel, then the rotating pneumatic tire is braked until it re-establishes contact.
Automatically brakes individual wheels - ESP
ESP stabilizes motion parameters in the boundary zones of dynamic properties. It supports the driver with its targeted brake engagement on individual wheels or engine management corrections in regards to keeping your vehicle on course. However, in spite of all the theoretical premises (dreams) on absolute safety - the boundaries of the physics of motion cannot be established by ESP: where it fails from the very beginning «head», even the most advanced automotive electronics «will be on the sidelines».
Brakes Mondeo
The Ford Mondeo slows down with four disc brakes. Front, with internal ventilation, discs have a thickness of 24 mm and a diameter of 300 mm. 60mm pistons take them «in pincers». On the rear axle are discs with a thickness of 12 mm and a diameter of 280 mm, which are acted upon by pistons measuring 36 millimeters.
In order for the floating brackets to receive the correct «bite», the Mondeo has a brake booster that is directly connected to the brake pedal. Direct contact with the brake pedal also saves on the intermediate lever. Mondeo driver notices «missing part» at a comfortable pressure point and well-dosed generation of pressure in the brake system.
ABS in combination with EDB is also standard on the Mondeo braking system. EDB uses ABS sensors to detect wheel speeds. During the braking process, the EDB controlled rear wheels «attached» always so much brake pressure that they always brake close to the blocking limit with maximum decelerating force. The system automatically takes into account the corresponding load condition and reduces the braking distance even outside the ABS control range.
The Mondeo ABS system, with its twelve control intervals per second, is state of the art. It provides, with unrestricted handling, maximum deceleration and forms the basis for TCS and ESP.
TCS in low speed ranges brakes only individual wheels. On the other side 50 km/h TCS optional «worries» engine management: it cuts further by selecting cylinders «fuel diet» and/or modified ignition timings and torque until a regular traction ratio dominates on the drive wheels again.
Additionally evaluates Ford's Mondeo undercarriage safety margins using ESP. How the interactive ESP system reduces engine power on a progressive scale and purposefully brakes an individual wheel. ESP «provokes» their «capture» yaw moment that automatically stabilizes the vehicle. The system works completely autonomously with its own «active» brake booster.
At this point, we will consciously repeat for you: «headless» ESP drivers do not create airbags - if the boundaries of the physics of movement are exceeded, then «departure» - even with ESP - inevitable.
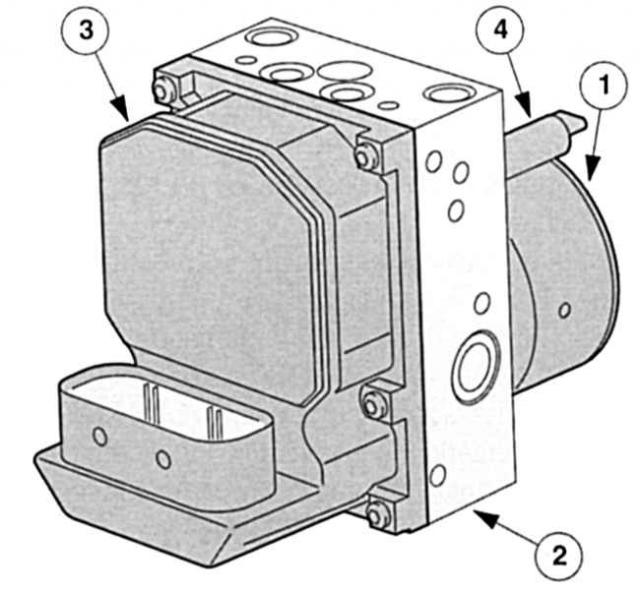 Four channels, twelve valves, control electronics for ABS, TCS, EBD: ESP block. 1 - Self-priming 2-circuit hydraulic pump,
|
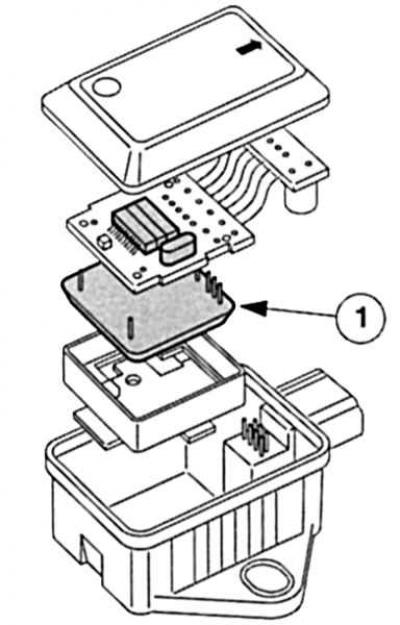 Hull - two functions: yaw rate and lateral acceleration sensor. 1 dual sensor unit. |
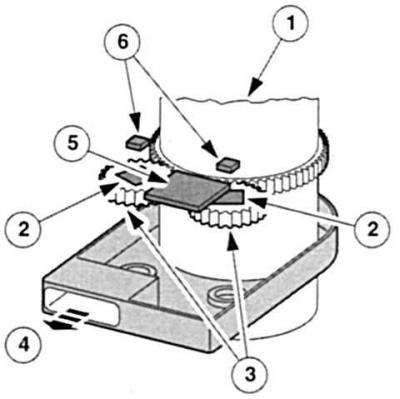 Accurate measurement: steering wheel angle sensor. 1 - steering column,
|
Overview - elements of the braking system
Brake system with double-circuit hydraulic drive (predominantly with diagonally divided hydraulic drive):
Accordingly, a separate brake circuit is established by connecting the front wheel and the diagonally opposite rear wheel.
Master brake cylinder (GTZ): Converts the mechanical force of the brake pedal into hydraulic force. It takes care of the rapid decrease in pressure in the system after releasing the pedal.
Brake booster (servo brake): Located in the engine compartment in front of the master brake cylinder. With each braking process, it increases the mechanical force of pressure on the pedal by about 60%. In vehicles with ESP, it is installed «active» brake booster. As soon as the electronic stabilization program starts in the Mondeo, the solenoid valve in the amplifier is activated. This creates a pressure of around 10 bar on the back of the membrane even without depressing the brake pedal. The brake booster gets its «energy» via a hose directly from the intake manifold or a separate vacuum pump (diesel). When braking, the diaphragm connected by a piston to the GTZ reacts to the difference between the pressure of the outside air and the low pressure in the intake manifold.
Wheel brake cylinder (KTC): brake fluid pressure in the CTC can reach 120 bar. CTC pistons transmit pressure to the pipeline system to the free pistons in the disc brake calipers (disc brake) or wheel brake cylinders (drum brake). The piston stroke in disc brakes is transmitted to the discs by brake pads or in drum brakes by brake linings to the drum.
| TECHNICAL DICTIONARY | ||||
|
Checking the brake system - in case of strong doubt, an option for the workshop
On every meter of public highways, the braking system is responsible for your safety and the safety of other road users. Hence the conclusion: functioning brakes are life insurance. Therefore, do not be afraid to remove the wheels from time to time and check the condition of the brake linings and discs. Maintenance work on the brake system is not that difficult. However «put your hands on the brakes only if», if you are absolutely convinced: at the slightest doubt «give your brakes» better than a special workshop, which everyone knows «know-how» and where can I find the necessary tool.
Visitor comments