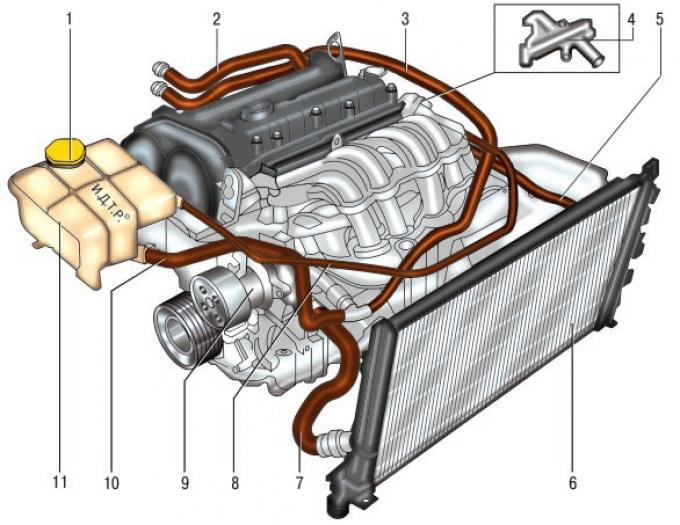
Pic. 5.58. Cooling system: 1 - plug of the expansion tank; 2 - heater supply hose; 3 - the outlet hose of the heater; 4 - distributor body; 5 – the inlet hose of a radiator; 6 - radiator; 7 - outlet hose of the radiator; 8 - steam outlet hose of the expansion tank; 9 - water pump; 10 – a liquid hose of a broad tank; 11 - expansion tank.
The engine cooling system is liquid, closed type, with forced circulation of liquid. The device of the cooling system is shown in fig. 5.58. The system consists of a cooling jacket, a radiator 6 with an electric fan, an expansion tank 11, a water pump 9, a thermostat, a water jacket outlet pipe and hoses.
The circulation of fluid in the system creates a water pump. From the pump, liquid is supplied to the engine cooling jacket, washes the combustion chamber cylinders and then enters the thermostat. Depending on the position of the thermostat valve, the liquid enters either the water pump (at low temperature), or into the radiator (at high temperature).

Radiator with a horizontal fluid flow, with a tubular-ribbon aluminum core and plastic tanks.
There is a drain plug at the bottom of the left radiator tank. In the tanks there are inlet and outlet pipes of hoses to the water jacket of the engine, a pipe of a steam hose connecting the radiator with the expansion tank.

Expansion tank serves to compensate for the changing volume of the coolant depending on its temperature. It is made of translucent plastic. In the plastic stopper of the tank, which closes its neck, inlet and outlet valves are installed.
NOTE: The serviceability of the expansion tank plug valves is very important for the normal operation of the cooling system. However, if problems arise (e.g. boiling coolant) motorists pay attention only to the operation of the thermostat and forget to check the valves.

Leakage of the exhaust valve leads to a decrease in the boiling point of the coolant, and its jamming in the closed state leads to an emergency increase in pressure in the system, which can cause damage to the radiator and hoses.

Water pump centrifugal type provides forced circulation of liquid in the cooling system. It is located on the front surface of the cylinder block and is driven from the crankshaft pulley by a V-ribbed belt common to the generator and power steering pump. The pump has sealed bearings that do not require relubrication. The pump cannot be repaired, therefore, in case of failure (fluid leakage or bearing damage) it is replaced as an assembly.

The thermostat, which is a solenoid valve, maintains the normal operating temperature of the coolant and reduces the warm-up time of the engine.
The thermostat is controlled by an electronic engine control unit, which receives information from a coolant temperature sensor installed on the outlet pipe of the water jacket. The thermostat is installed in a housing fixed to the cylinder head. At a coolant temperature of up to 60°C, the thermostat is completely closed and the liquid circulates through a small circuit, bypassing the radiator, which accelerates the engine warm-up. At a temperature of about 80°C, the thermostat begins to open, and at 98°C it opens completely, providing fluid circulation through the radiator.

Electric fancooling system (with plastic eight-bladed impeller) serves for additional airflow of the radiator, turns on and off at the signal of the electronic engine control unit. Moreover, depending on the intensity of the thermal regime and the algorithm of the air conditioner, the electric fan can rotate at low and high speeds. Changing the fan speed is provided by the engine control unit by connecting an additional resistance. The electric fan assembly with the casing is fixed to the radiator of the cooling system.
Water jacket outlet serves to distribute coolant flows depending on the operating modes of the cooling system. A coolant temperature sensor is screwed into the body of the pipe, according to which the electronic unit of the engine control system controls the thermal regime of the engine.
Check valve (do not install on Duratec-HE engines) Designed to stop the removal of coolant to the expansion tank when starting a cold engine. The shut-off valve, when closed, reduces coolant circulation in the cold engine system, which saves fuel when the engine warms up and reduces warm-up time. At a coolant temperature of 80°C, the shut-off valve opens fully and coolant begins to circulate through the expansion tank.
The radiator for the interior heater is also included in the cooling system with hoses.
The system is filled with liquid (antifreeze), that does not freeze at ambient temperatures down to -40°C. Type of coolant filled in the cooling system - Motorcraft Super Plus 4 (Green colour) or Motorcraft Super Plus 2000 (orange color).
WARNING: Non-silicified organic acid based Motorcraft Super Plus 4 fluid (OAT), should not be mixed with other types of coolant.
Motorcraft Super Plus 2000 is based on monoethylene glycol, like most modern coolants.
WARNING: It is not recommended to fill the cooling system with water, as antifreeze contains anti-corrosion, anti-foam and anti-scale additives.
Coolant is toxic! Avoid inhalation of vapors and contact with skin.
Timely eliminate the violation of the tightness of the cooling system in order to avoid the ingress of coolant vapor into the vehicle interior during its operation.
Your health is more valuable than a new cooling system pipe or a tube of sealant! The electronic engine control unit contains a program to protect the engine from overheating. At the very beginning of overheating, according to information from the coolant temperature sensor, the engine control unit sends a command to move the arrow of the coolant temperature gauge to the red zone.
If the driver does not stop the engine and its temperature continues to rise, the engine control unit turns on a warning light that warns the driver that the engine is approaching a critical limit and must be stopped.
If the driver ignores the readings of the coolant temperature gauge and the activation of the warning light, the electronic engine control unit cuts off the fuel supply to two engine cylinders and limits the engine speed to 3000 rpm-1.
At the same time, the engine malfunction warning light comes on, which indicates the possibility of significant engine damage and a sharp increase in exhaust toxicity. This mode draws air into the deactivated cylinders to reduce engine temperature. Moreover, the disconnected cylinders alternate with each other for more uniform cooling.
NOTE: If the engine has gone into 2-cylinder only mode, the only way to return it to 4-cylinder mode is by turning the ignition off and on again.
If the engine temperature continues to rise even after all the measures taken, the control unit stops the engine. If at this time the throttle pedal is moved by pressing the foot to a large angle (For example, the driver is overtaking), the engine will stop only 10 seconds after the pedal is released.
Visitor comments