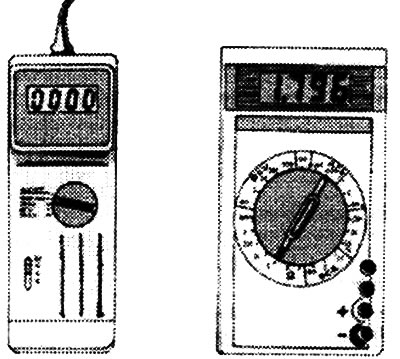
For motorists, there are combined measuring instruments that are specially designed for carrying out control work in a car. Using such a device, you can measure the shaft speed in a car, the angle of the closed state of the contacts of the ignition system breaker and voltages up to 20 V. When measuring resistance, the device is usually limited to a range in kiloOhms. In addition to this, measuring instruments are used to test electrical and electronic components. They allow a wide range of measurements from low resistances in ohms up to the megaohm range. Voltage can be measured very accurately (IN), which is primarily required for checking electronic structural elements.
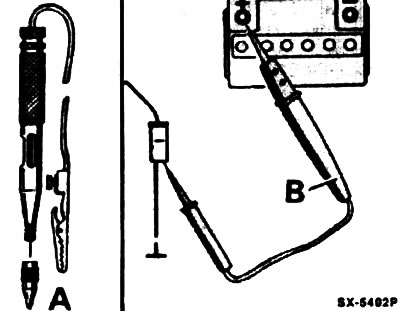
If you only need to check whether voltage is applied at all (V), then a simple control light is suitable for this (A). True, this is valid only for those electrical circuits in which there are no electronic parts. Nevertheless, electronic parts are extremely sensitive to too high currents. Under certain circumstances, they can fail even when a control light is connected.
Attention! When checking electronic parts (transistors, diodes and control nodes) it is necessary to use a high-resistance voltage indicator (IN). It works in the same way as a control light, but without damaging the electronic components, and is suitable for all control operations.
Visitor comments