Main settings
Engine | 1,3 HC OHC | 1.6 NS ONS | 1.6 NS ONS economical | 2.0 NS ONS |
| engine's type | JCT | LCT | LCS | NET |
| Cylinder diameter (mm) | 79,02 | 87,67 | 87,67 | 90,82 |
| piston stroke (mm) | 66,00 | 66,00 | 66,00 | 76,95 |
| Volume (see3) | 1294 | 1593 | 1593 | 1993 |
| Compression ratio | 9,0 | 9,2 | 9,2 | 9,2 |
| Compression pressure (MPa) | 1,1 – 1,3 | 1,1 – 1,3 | 1,1 – 1,3 | 1,1 – 1,3 |
| Rated power: | ||||
| – kW at rpm | 44 at 5700 | 55 at 5300 | 55 at 5700 | 77 at 5200 |
| – HP at rpm | 60 at 5700 | 75 at 5600 | 75 at 5700 | 105 at 5200 |
| Max Torque (Nm at rpm) | 98 at 3100 | 120 at 2900 | 120 at 2900 | 157 at 4000 |
Cylinder head
The head is made of a special alloy and has valve seats molded directly into the material of the cylinder head.
| Designation: | |
| – 1.3 dm engine3 | 3 |
| – 1.6 dm engine3 | 6 |
| – 2.0 dm engine3 | 0 |
| Valve contact angle | 44°30' – 45° |
| Valve seat width: | |
| - inlet | 1.5mm |
| - graduation | 2.0 mm |
| Maximum grinding depth of the lower plane of the cylinder head | 0.154 mm |
| Camshaft bearing bore diameters: | |
| - front bearing | 45.072 - 45.102 mm |
| – middle bearing | 47.692 - 47.772 mm |
| - rear bearing | 48.072 - 48.102 mm |
Cylinder head gasket
Brand: Reinz.
Valve guides
The guide holes are made directly in the cylinder head.
| Nominal diameter | 8.063 - 8.088 mm |
| Repair size: | |
| – exceeding 0.2 | 8.263 - 8.288 mm |
| – exceeding 0.4 | 8.463 - 8.488 mm |
Valves
The valves are installed in the cylinder head and inclined at an angle of 7°30' to the cylinder axis.
Valve sizes (mm)
Engine | 1.3 dm3 | 1.6 dm3 | 2.0 dm3 |
| Inlet valve: | |||
| - length | 112,65 – 113,65 | 112,65 – 113,65 | 110,65 – 111,65 |
| - plate diameter | 38,30 – 38,70 | 41,80 – 42,20 | 41,80 – 42,20 |
| Exhaust valve: | |||
| - length | 112,05 – 113,75 | 112,05 – 113,75 | 110,10 – 112,05 |
| - plate diameter | 29,80 – 30,20 | 34,00 – 34,40 | 35,80 – 36,20 |
Inlet valve sizes are common to all engines.
Rod diameter
| Nominal | 8.025 - 8.043 mm |
| Repair size +0.2 | 8.225 - 8.243 mm |
| Repair size +0.4 | 8.425 - 8.443 mm |
| Repair size +0.6 | 8.625 - 8.643 mm |
| Repair size +0.8 | 8.825 - 8.843 mm |
Exhaust valve sizes are common to all engines.
Rod diameter
| Nominal | 7.999 - 8.017 mm |
| Repair size +0.2 | 8.199 - 8.217 mm |
| Repair size +0.4 | 8.399 - 8.417 mm |
| Repair size +0.6 | 8.599 - 8.617 mm |
| Repair size +0.8 | 8.799 - 8.817 mm |
The gap of the rod in the guide is 0.046–0.089 mm.
| Valve clearance (with a cold engine): | |
| - inlet valve | 0.20 mm |
| - Exhaust valve | 0.25 mm |
Valve springs
The same springs are used for intake and exhaust valves.
| Spring diameter | 23.445 - 23.95 mm |
| Spring wire diameter | 3.87 - 3.93 mm |
| Number of turns | 4,7 |
| free length | 47.00 mm |
Engine block
The engine block is cast iron. The cylinders are made directly in the cylinder block.
| Support bearing width | 27.17 - 27.22 mm |
| Internal diameters of main bearings (measured vertically): | |
| - nominal | 57.000 - 57.034 mm |
| - repair size -0.25 | 56.750 - 56.784 mm |
| – repair size -0.50 | 56.500 - 56.534 mm |
| – repair size -0.75 | 56.250 - 56.284 mm |
| – repair size -1.00 | 56.000 - 56.034 mm |
| Bore diameters of the main bearing seats in the cylinder block: | |
| - nominal size | 60.620 – 60.640 mm |
| – repair size +0.4 | 61.020 – 61.040 mm |
Cylinder diameters (mm)
Engine | 1.3 dm3 | 1.6 dm3 | 2.0 dm3 |
Designation | 13 | 16 | 20 |
| Nominal standard diameters: | |||
| – group 1 | 79,000 – 79,010 | 87,650 – 87,660 | 90,800 – 90,810 |
| – group 2 | 79,010 – 79,020 | 87,660 – 87,670 | 90,810 – 90,820 |
| – group 3 | 79,020 – 79,030 | 87,670 – 87,680 | 90,820 – 90,830 |
| – group 4 | 79,030 – 79,040 | 87,680 – 87,690 | 90,830 – 90,840 |
| Nominal diameters with tolerance: | |||
| – group A | 79,510 – 79,520 | 88,160 – 88,170 | 91,310 – 91,320 |
| - group B | 79,520 – 79,530 | 88,170 – 88,180 | 91,320 – 91,330 |
| - group C | 79,530 – 79,540 | 88,180 – 88,190 | 91,330 – 91,340 |
| Repair dimensions: | |||
| – standard | 79,030 – 79,040 | 87,680 – 87,690 | 90,830 – 90,840 |
| - with a tolerance of 0.5 | 79,530 – 79,540 | 88,180 – 88,190 | 91,330 – 91,340 |
| – with a tolerance of 1.0 | 80,030 – 80,040 | 88,680 – 88,690 | 91,830 – 91,840 |
Crank mechanism
Crankshaft
The steel crankshaft is supported by five bearings.
| Axial play | 0.08 - 0.28 mm |
| Diameters of main journals: | |
| - nominal size | 56.970 - 56.990 mm |
| - repair size -0.25 | 56.720 - 56.740 mm |
| – repair size -0.50 | 56.470 - 56.490 mm |
| – repair size -0.75 | 56.220 - 56.240 mm |
| – repair size -1.00 | 55.970 - 55.990 mm |
| Clearance in main bearings | 0.010 - 0.064 mm |
| The measurement is carried out using Plastigage measuring rods. | |
| Connecting rod diameters: | |
| - nominal size | 51.980 – 52.000 mm |
| - repair size -0.25 | 51.730 – 51.750 mm |
| – repair size -0.50 | 51.480 – 51.500 mm |
| – repair size -0.75 | 51.230 – 51.250 mm |
| Thickness of thrust half rings: | |
| - nominal size | 2.30 - 2.35 mm |
| - repair size | 2.50 - 2.55 mm |
Flywheel
The flywheel is fixed to the crankshaft flange with six bolts.
Intermediate shaft
The intermediate shaft is located in front of the cylinder block, on the left side. Provides a drive for the ignition distributor, as well as oil and fuel pumps.
Axial clearance - 0.050–0.204 mm.
Connecting rods
The connecting rods are forged from steel and have an I-beam profile in their cross section. The piston pin is pressed into the connecting rod head.
| Connecting rod head bore diameter | 23.964 - 23.976 mm |
| Pin tension in the connecting rod head: | 0.018 - 0.039 mm |
| Heating temperature of the connecting rod head during pin installation | 250 - 300°С |
| Connecting rod bore diameter | 55.000 – 55.020 mm |
| The inner diameters of the holes of the connecting rod bearings: | |
| - nominal size | 52.006 - 52.044 mm |
| - repair size -0.25 | 51.756 - 51.794 mm |
| – repair size -0.50 | 51.706 - 51.744 mm |
| – repair size -0.75 | 51.256 - 56.294 mm |
| – repair size -1.00 | 51.006 - 51.044 mm |
| Clearance in main bearings | 0.006 - 0.064 mm |
The measurement is carried out using Plastigage measuring rods. | |
| Permissible non-perpendicularity of the axis of the holes relative to the axis of the connecting rod: | |
| - head hole | 0.10 mm |
| - base hole | 0.15mm |
Pistons
The pistons are made of light alloy, without grooves on the conductive part, with a cast invar ring to limit thermal dimensional errors. In the upper part there are three grooves for piston rings. The axis of the piston pin hole is offset relative to the piston axis. Pistons are supplied in kits with pins and connecting rods.
Installation Method: The arrow on the bottom of the piston must point towards the front of the engine (towards the drive of the gas distribution system).
Piston pins
Pins made of alloy steel and heat treated are pressed into the connecting rod heads (hot mounting at head temperature 250°–300°С) and rotate in the piston hubs.
| Length: | |
| – engine 1.3 dm3 | 60.0 - 60.8 mm |
| – engine 1.6 dm3 | 68.0 - 68.8 mm |
| – engine 2.0 in.3 | 72.0 - 72.8 mm |
| Diameter: | |
| - marking in red | 23,994 – 23,997 |
| - marked in blue | 23,997 – 24,000 |
| - marking in red | 22,000 – 24,003 |
| Clearance in piston hubs | 0.008 - 0.014 mm |
| Tension in the connecting rod head | 0.018 - 0.039 mm |
Piston dimensions (mm)
Engine | 1.3 dm3 | 1.6 dm3 | 2.0 dm3 |
| Nominal standard diameters: | |||
| – group 1 | 78,965 – 78,975 | 87,615 – 87,625 | 90,765 – 90,775 |
| – group 2 | 78,975 – 78,985 | 87,625 – 87635 | 90,775 – 90,785 |
| – group 3 | 78,985 – 78,995 | 87,635 – 87,645 | 90,785 – 90,795 |
| – group 4 | 78,995 – 79,005 | 87,645 – 87,655 | 90,795 – 90,805 |
| Repair dimensions: | |||
| – standard | 78,900 – 79,015 | 87,640 – 87,665 | 90,780 – 90,805 |
| - with a tolerance of 0.5 | 79,490 – 79,515 | 88,140 – 88,165 | 91,280 – 91,305 |
| – with a tolerance of 1.0 | 79,990 – 80,015 | 88,640 – 88,665 | 91,780 – 91,805 |
| Clearance of new pistons in cylinders | 0,015 – 0,050 | 0,015 – 0,050 | 0,025 – 0,060 |
Piston rings
Each piston has three rings: two sealing and one oil scraper.
| O-ring lock clearance (located in the cylinder): | |
| – engine 1.3 in.3 and engine 1.6 in.3 | 0.30 - 0.50 mm |
| – engine 2.0 in.3 | 0.038 - 0.048 mm |
| Clearance of the lock of an oil scraper ring | 0.40 - 1.40 mm |
Location of ring locks:
- sealing – 150°each (in opposite directions) regarding the lock of the oil scraper ring;
- oil scraper - the lock of the expanding spring is installed in accordance with the direction of the arrow on the bottom of the piston; the locks of the upper and lower plates are set 25 mm to the right and left of the direction of the arrow.
Gas distribution system
Four-cylinder in-line engine ONS (general form)
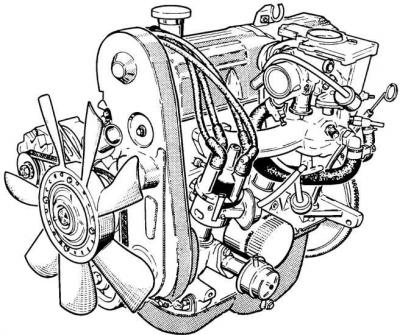
The camshaft is located in the cylinder head, drives the valves through the valve lever and is driven by a toothed belt.
Valve clearance (cold):
- intake: 0.20 mm;
- graduation: 0.25 mm.
Distribution phases
| Engine | 1.3 dm3 and 1.6 dm3 | 2.0 dm3 |
| OZD | 22°before TDC | 24°before TDC |
| ZZD | 54°after BDC | 64°after BDC |
| OZW | 64°before BDC | 70°before BDC |
| ZZW | 12°after TDC | 18°after TDC |
OZD and ZZD - opening and closing of the intake valve, respectively;
OZW and ZZW - opening and closing of the exhaust valve, respectively;
TDC and BDC are top and bottom dead center respectively.
Toothed belt
| Brand: Ford Powergrip | Type: |
| – engine 1.3 dm3 | 70NM 6288 AA |
| – engine 1.6 dm3 | 70NM 6288 AA |
| – engine 2.0 dm3 | 70NM 6268 AA |
| Number of teeth | |
| – engine 1.3 dm3 | 119 |
| – engine 1.6 in.3 | 119 |
| – engine 2.0 dm3 | 122 |
Camshaft
The camshaft rotates in three bearings.
| Camshaft bearing diameters: | |
| - front | 41.987 - 42.013 mm |
| – medium | 44.607 - 44.633 mm |
| - rear | 44.987 - 45.013 mm |
| Inner diameters of bearing bushes: | |
| - front | 42.035 - 42.055 mm |
| – medium | 44.655 - 44.675 mm |
| - rear | 45.035 - 45.055 mm |
| Camshaft end play | 0.104 - 0.204 mm |
| Thickness of camshaft thrust pads | 3.96 - 4.01 mm |
| Cam lift: | |
| – engine 1.3 dm3 | 5.9639 mm |
| – engine 1.6 dm3 | 5.9639 mm |
| – engine 2.0 dm3 | 6.3323 mm |
| Jaw height: | – engine 1.3 dm3 | 35.894 - 36.234 mm | – engine 1.6 in.3 | 35.894 - 36.234 mm |
| – engine 2.0 dm3 | 36.260 – 36.600 mm |
Visitor comments