The principle of operation of the impulse sensor with a Hall converter
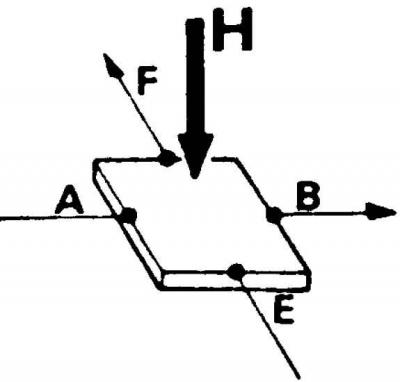
A and B are control electrodes, H is the direction of the magnetic field (perpendicular to the surface), E and F - electrodes, between which there is a potential difference (hall voltage)
If the corresponding semiconductor through which the current flows between the electrodes (A) And (IN), will be subjected to a magnetic field (H), then between the electrodes (E) And (F) this semiconductor, there will be a potential difference. This phenomenon is called the Hall effect.
Visitor comments