2. Check the block visually for cracks, rust, corrosion. Check if the threads in the threaded holes are clogged.
3. Check up internal surfaces of cylinders on attrition and scratches.
4. Measure the diameter of each cylinder at the top (just below the ledge), in the central part and below, parallel to the axis of the crankshaft (see picture).
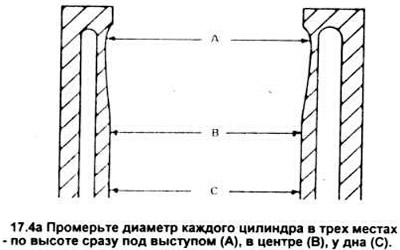

Then measure the diameter of each cylinder at the same three levels perpendicular to the axis of the crankshaft. Compare your results with the specification data. If the cylinder walls are badly worn, scratched, have too large deviations from roundness or taper above the allowable, carry out additional boring and honing of the block holes. After processing, pistons and rings of large sizes will be required.
5. If the condition of the cylinders is not bad, the dimensions do not go out of tolerance and the required clearance between the piston and the cylinder is maintained, only honing is necessary.
Visitor comments