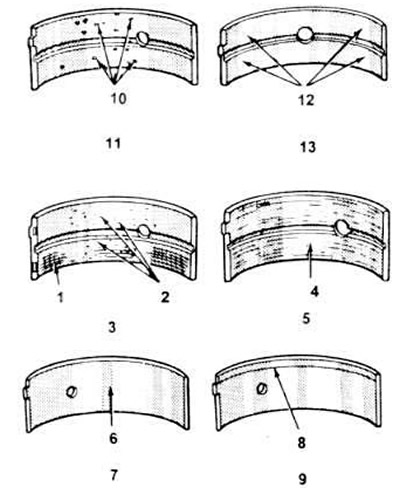
21.1. Bearing failure diagnostics.
1 scratches.
2. The introduction of dirt into the bearing material.
3. Scratched by foreign matter.
4. Coating worn off.
5. Lack of oil or incorrect clearance adjustment.
6. Coating has come off at the edges.
7. Hourglass effect.
8. Radial movement.
9. Radial movement.
10. Pits or shells.
11. Fatigue failures.
12. Sections glisten (polished).
13. Incorrect installation.
2. Bearings are destroyed due to lack of oil, dirt and foreign particles, motor overload and corrosion. Regardless of the type of cause of bearing failure. it must be eliminated so that it does not appear in the newly assembled engine.
3. To check the bearings, remove them from the block, separate the covers, connecting rods and connecting rod caps, then lay them on a clean surface in the same position in which they were in the engine. This will help you immediately identify defects in bearings and the corresponding crankshaft journals.
5. Disadvantage (or lack) oil can occur for a number of internal reasons. Excessive overheating (reduces oil layer), overload (squeezes oil from the working surfaces of the bearing), as well as oil leaks or splashes of it (due to excessive bearing clearances, worn oil pump or too high engine speeds) - all this leads to an emergency lack of oil. Often, due to misalignment of the oil-conducting holes in the bearing housing, they are clogged; and this leads to oil "fasting" bearing, and as a result, to damage it. If the bearing fails due to lack of oil, then usually in this case its material is pressed or rubbed away from the steel base of the bearing.
6. Certain driving habits also affect bearing life. Full throttle at low speed (engine overload) seriously overloads the bearings - this is the reason "push-ups" oil film. Such loads cause the bearing to bend, which leads to cracks in the running surfaces (fatigue wear). Ultimately, the bearing material breaks off in pieces from the steel base. Driving very short distances also contributes to bearing corrosion because the engine does not heat up enough to evaporate water condensation and corrosive compounds. These products collect in engine oil, forming acid and deposits. Once the oil enters the engine bearings, the acid reacts with the bearing material and causes it to corrode.
7. Incorrect installation of bearings during engine assembly also leads to the destruction of bearings. Fitting bearings that are too tight will leave insufficient clearance for the oil supply, causing them to lubricate "starvation". Dirt and foreign inclusions that have fallen on the liner lead to the appearance of spots, and in the future - to destruction.
Visitor comments